Home > Press > NSF Funds Innovative Approach to Biomimetic Nanofiber Bone Regeneration
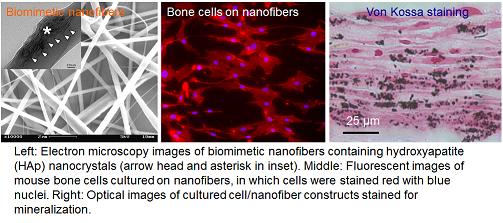 |
Abstract:
Every year nearly 6.2 million bone fractures occur in the United States as a result of trauma and disease. Current standards for bone repair can lead to rapid bone fusion but with limited mechanical strength often due to the lack of cortical bone tissue which is difficult to harvest without pain and severe morbidity. Funded by the National Science Foundation, Dr. Hongjun Wang, a professor in the Department of Chemistry, Chemical Biology and Biomedical Engineering at Stevens Institute of Technology and his collaborators have developed a revolutionary "bottom-up" approach for reconstructing intricate bone tissue with the potential to form hierarchical cortical bone.
NSF Funds Innovative Approach to Biomimetic Nanofiber Bone Regeneration
Hoboken, NJ | Posted on August 8th, 2010Dr. Wang's research project, "Biomimetic Creation of Cortical-like Bone with Hierarchical Structure," will develop robust, controllable and effective platforms for the creation of tissues with complex and hierarchical structure for potential applications in reconstructive and transplant surgery.
Biomimetics is the study and development of synthetic systems that mimic the formation, function, or structure of biologically produced substances, materials, mechanisms and processes. Wang's research team is part of a thriving tissue engineering industry that uses a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physio-chemical factors to repair or replace portions of damaged tissues.
In contrast to current state-of-the-art research that focuses on creating highly porous cancellous bone, Dr. Wang focuses on engineering cortical bone, the major load bearing component. He takes a modular approach to generating dense cortical bone by synthesizing osteon-like repeating units and fusing these units together to form large, compacted cortical-like bone tissue. This "bottom-up" methodology uses nanotechnology to enable the development of scaffolds that focus on the smallest level possible and build upward. Incorporating nanofibers into bone tissue engineering to form the small cortical bone repeating units, these biomimetic scaffolds offer large surface areas and well-interconnected pores for nutrient transport and cell penetration, and more importantly, provide a biomimetic cell-friendly microenvironment to facilitate the bone tissue formation, needed for successful repair of large bone defects.
"The results of Dr. Wang's research will have a far-reaching impact on tissue engineering," says Dr. Michael Bruno, Dean of the Schaefer School of Engineering and Science. "The wealth of basic and applied knowledge learned at Stevens will lay the foundation for our long-term research efforts and the development of real-world applications."
Over the next-three years, Dr. Wang's research team plan to make substantial strides in synergistically integrating nanobiomaterials with bone tissue engineering for the creation of cortical bone with hierarchical structure and functional complexity.
"We hope to establish a family of biomimetic nanofibers containing collagen and calcium phosphate to support the phenotype of bone-forming cells; new practical approaches to creating osteon-like units using biomimetic nanofibers and osteoblasts; formulation of calcium phosphate containing collagen gel for bone tissue formation; and most importantly, an innovative approach to generating cortical-like bone by assembling osteon-like structures into one fused construct," explains Dr. Wang.
"The intellectually rich environment established by Dr. Wang and his team is inspiring to our graduate and undergraduate students who are participating in the transformative benefits of cutting-edge research and its profound application," says Dr. Philip Leopold, Director of the Department of Chemistry, Chemical Biology and Biomedical Engineering.
For more information on Stevens Pioneering Bone Regeneration research, please contact Dr. Wang:
www.stevens.edu/research/research_profile.php?fac_id=16
####
About Stevens Institute of Technology
Founded in 1870 and celebrating 140 Years of Innovation, Stevens Institute of Technology, The Innovation University TM , lives at the intersection of industry, academics and research. The University's students, faculty and partners leverage their collective real-world experience and culture of innovation, research and entrepreneurship to confront global challenges in engineering, science, systems and technology management.
Based in Hoboken, N.J. and with a location in Washington, D.C., Stevens offers baccalaureate, master’s, certificates and doctoral degrees in engineering, the sciences and management, in addition to baccalaureate degrees in business and liberal arts. Stevens has been recognized by both the US Department of Defense and the Department of Homeland Security as a National Center of Excellence in the areas of systems engineering and port security research. The University has a total enrollment of more than 2,200 undergraduate and 3,700 graduate students with almost 450 faculty. Stevens’ graduate programs have attracted international participation from China, India, Southeast Asia, Europe and Latin America as well as strategic partnerships with industry leaders, governments and other universities around the world. Additional information may be obtained at www.stevens.edu and www.stevens.edu/press.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Office of University Communications
+1-201-216-5116
Copyright © Stevens Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








