Home > Press > Nanoparticles Increase Intensity of Quantum Dots' Glow
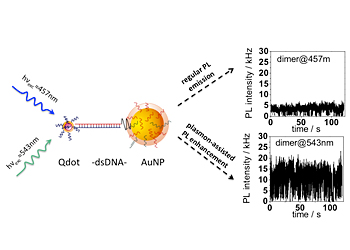 |
| Photoluminescence enhancement is demonstrated at the single molecule level for two-particle systems composed of a quantum dot (Qdot) and gold nanoparticle (AuNP) linked by double stranded DNA (dsDNA) when optically excited with wavelengths within the surface plasmon resonance range of the gold nanoparticle. |
Abstract:
Demonstration of precision DNA-based nanoassembly method could lead to advances in solar cells, optoelectronics, and biosensors
Nanoparticles Increase Intensity of Quantum Dots' Glow
Upton, NY | Posted on July 26th, 2010By linking individual semiconductor quantum dots with gold nanoparticles, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have demonstrated the ability to enhance the intensity of light emitted by individual quantum dots by up to 20 times. The precision method for making the light-emitting particle clusters published online July 26, 2010 in the journal ChemComm will greatly advance scientists' ability to study and modify the optical properties of quantum dots, and could eventually lead to improved solar energy conversion devices, light-controlled electronics, and biosensors.
"Quantum dots tiny crystals of semiconductor materials that fluoresce, or emit light, in response to photoexcitation have enormous potential for use in a wide range of fields from solar energy conversion to computing and medicine," said Mircea Cotlet, a physical chemist at Brookhaven's Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) and lead author on the current study. "But many factors can influence the light they emit, and it's hard to sort out the contributions of these factors in large samples due to the inherent ensemble averaging. Building single-molecule structures at the CFN seemed the ideal way to tease out these effects."
The Brookhaven team recently developed a precision technique for building such nano-sized structures using short strands of DNA as a highly specific "glue" to link particles together.
"DNA consists of two strands with complementary pairings of bases that stick together in only one way," explained Oleg Gang, leader of the team that developed the technique. "By varying the length of the individual strands and attaching complementary pieces to the particles we want to join, and anchoring the whole process on an assembly surface, we can precisely control the construction of individual nanoclusters."
In the current study, the team used this multi-step process to attach semiconductive quantum dots to gold nanoparticles. Metallic materials are known to affect the optical properties of quantum dots, either by enhancing or inhibiting photoluminescence, depending on a range of factors including the size and shape of the materials, the distance between them, and the wavelength of light used to induce photoexcitation.
The precision assembly technique allowed the scientists to control the size, shape, and distance factors to a high degree of precision and test the effect of wavelength in isolation. They specifically chose two wavelengths to test: one close to the so-called "plasmon resonance" of the gold nanoparticles that is, a wavelength that induces a collective oscillation of the material's conductive electrons, leading to strong absorption of light at that wavelength and one outside this range.
The wavelength within the plasmon resonance range enhanced photoluminescence approximately four-fold when compared with the luminescence achieved by the wavelength outside the plasmon resonance range. When compared with the photoluminescence of individual quantum dots not linked to gold nanoparticles, the resonant wavelength enhanced photoluminescence of the gold-linked quantum dots by an order of magnitude.
"This ability to control the excitonic properties in plasmonic fluorescent quantum dots is essential to the development of devices such as solar cells, light emitting diodes, or optical circuits and might improve the sensitivity of quantum-dot based biosensing assays," Cotlet said.
In addition to Mircea Cotlet and Oleg Gang from Brookhaven, Mathew Maye (now at Syracuse University) contributed to this work. The research was performed at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials at Brookhaven National Laboratory and was supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy.
The Center for Functional Nanomaterials at BNL is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale that are supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories.
Related Links
*DNA-Based Assembly Line for Precision Nano-Cluster Construction:
www.bnl.gov/bnlweb/pubaf/pr/PR_display.asp?prID=921
BNL's CFN: www.bnl.gov/cfn/
DOE NSRCs: nano.energy.gov
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit, applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen McNulty Walsh
(631) 344-8350
Peter Genzer
(631) 344-3174
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NISTs grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NISTs grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








