Home > Press > UT researchers develop anthrax sensor
 |
Abstract:
Nanotechnologists at University of Twente's MESA+ research institute have developed a sensor that can detect anthrax spores. The invention is more sensitive and efficient than existing detection methods. The research is being published in the leading scientific journal Angewandte Chemie.
UT researchers develop anthrax sensor
The Netherlands | Posted on July 19th, 2010Anthrax - notorious as the powder ingredient in letter-bombs - is an infectious and potentially fatal disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. This bacterium produces spores - dried bacteria with a hard shell - that can survive long-term in the open air. University of Twente researchers have now designed a sensor that can detect a biomarker of the spores and thus determine their presence in a concentration one thousand times lower than the known toxic level.
Techniques for detecting anthrax spores (such as fluorescence and mass spectroscopy) already exist, but the UT sensor is much more sensitive and effective than any of them. It can also be reused in subsequent trials.
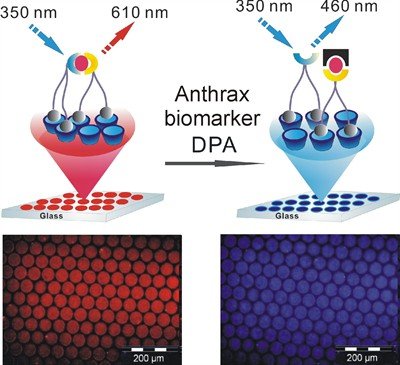
How the sensor works
Like other detection techniques, the UT sensor measures the presence of dipicolinic acid (DPA), a substance that accounts for between five and fifteen per cent of the dry weight of the spores. The sensor consists of a glass plate to which DPA-sensitive receptors have been attached. When the receptors are brought into contact with anthrax spores, the DPA binds with them. The concentration of the spores can be calculated with fluorescence spectroscopy, by shining ultraviolet light on to the sensor. DPA-bonded receptors will absorb this light and emit blue light, whereas receptors that have no DPA bonding will emit red light. By measuring the ratio of red to blue light in a sample, it is possible to determine the concentration of anthrax spores. The advantage of the sensor is that it does not need calibrating and is more finely tuned than other current methods. The next step for the researchers is to convert the system into a 'lab-on-a-chip' which will make it possible to measure samples using a fully automatic on-off process.
Note to the press
The research is being conducted by the departments of Molecular Nanofabrication and Supramolecular Chemistry & Technology at University of Twente's MESA+ research institute. It has been made possible by NanoNed and the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO).
For further details or a digital copy of the article Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of an Anthrax Biomarker at Molecular Printboards, please contact our Science Information Officer Wiebe van der Veen +31(0)53 489 4424).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Science Information Officer
Wiebe van der Veen
+31(0)53 489 4424
Copyright © University of Twente
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








