Home > Press > Nano-sized light mill drives micro-sized disk
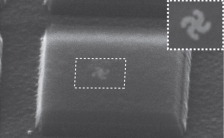 |
| This STM image shows a gammadion gold light mill nanomotor embedded in a silica microdisk. Inset is a magnified top view of the light mill. |
Abstract:
While those wonderful light sabers in the Star Wars films remain the figment of George Lucas' fertile imagination, light mills - rotary motors driven by light - that can power objects thousands of times greater in size are now fact.
Nano-sized light mill drives micro-sized disk
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 5th, 2010Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the University of California (UC) Berkeley have created the first nano-sized light mill motor whose rotational speed and direction can be controlled by tuning the frequency of the incident light waves. It may not help conquer the Dark Side, but this new light mill does open the door to a broad range of valuable applications, including a new generation of nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), nanoscale solar light harvesters, and bots that can perform in vivo manipulations of DNA and other biological molecules.
"We have demonstrated a plasmonic motor only 100 nanometers in size that when illuminated with linearly polarized light can generate a torque sufficient to drive a micrometre-sized silica disk 4,000 times larger in volume," says Xiang Zhang, a principal investigator with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and director of UC Berkeley's Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center (SINAM), who led this research. "In addition to easily being able to control the rotational speed and direction of this motor, we can create coherent arrays of such motors, which results in greater torque and faster rotation of the microdisk."
The success of this new light mill stems from the fact that the force exerted on matter by light can be enhanced in a metallic nanostructure when the frequencies of the incident light waves are resonant with the metal's plasmons - surface waves that roll through a metal's conduction electrons. Zhang and his colleagues fashioned a gammadion-shaped light mill type of nanomotor out of gold that was structurally designed to maximize the interactions between light and matter. The metamaterial-style structure also induced orbital angular momentum on the light that in turn imposed a torque on the nanomotor.
"The planar gammadion gold structures can be viewed as a combination of four small LC-circuits for which the resonant frequencies are determined by the geometry and dielectric properties of the metal," says Zhang. "The imposed torque results solely from the gammadion structure's symmetry and interaction with all incident light, including light which doesn't carry angular momentum. Essentially we use design to encode angular momentum in the structure itself. Since the angular momentum of the light need not be pre-determined, the illuminating source can be a simple linearly polarized plane-wave or Gaussian beam."
The results of this research are reported in the journal Nature Nanotechnology in a paper titled, " Light-driven nanoscale plasmonic motors." Co-authoring the paper with Zhang were Ming Liu, Thomas Zentgraf, Yongmin Liu and Guy Bartal.
It has long been known that the photons in a beam of light carry both linear and angular momentum that can be transferred to a material object. Optical tweezers and traps, for example, are based on the direct transfer of linear momentum. In 1936, Princeton physicist Richard Beth demonstrated that angular momentum - in either its spin or orbital form - when altered by the scattering or absorption of light can produce a mechanical torque on an object. Previous attempts to harness this transfer of angular momentum for a rotary motor have been hampered by the weakness of the interaction between photons and matter.
"The typical motors had to be at least micrometres or even millimeters in size in order to generate a sufficient amount of torque," says lead author Ming Liu, a PhD student in Zhang's group. "We've shown that in a nanostructure like our gammadion gold light mill, torque is greatly enhanced by the coupling of the incident light to plasmonic waves. The power density of our motors is very high. As a bonus, the rotational direction is controllable, a counterintuitive fact based on what we learn from wind mills."
The directional change, Liu explains, is made possible by the support of the four-armed gammadion structure for two major resonance modes - a wavelength of 810 nanometers, and a wavelength of 1,700 nanometers. When illuminated with a linearly polarized Gaussian beam of laser light at the shorter wavelength, the plasmonic motor rotated counterclockwise at a rate of 0.3 Hertz. When illuminated with a similar laser beam but at the larger wavelength, the nanomotor rotated at the same rate of speed but in a clockwise direction.
"When multiple motors are integrated into one silica microdisk, the torques applied on the disk from the individual motors accumulate and the overall torque is increased," Liu says. "For example, a silica disk embedded with four plasmonic nanomotors attains the same rotation speed with only half of the laser power applied as a disk embedded with a single motor."
The nanoscale size of this new light mill makes it ideal for powering NEMS, where the premium is on size rather than efficiency. Generating relatively powerful torque in a nanosized light mill also has numerous potential biological applications, including the controlled unwinding and rewinding of the DNA double helix. When these light mill motors are structurally optimized for efficiency, they could be useful for harvesting solar energy in nanoscopic systems.
"By designing multiple motors to work at different resonance frequencies and in a single direction, we could acquire torque from the broad range of wavelengths available in sunlight," Liu says.
This research was supported by DOE's Office of Science.
For more information about the research of Xiang Zhang visit xlab.me.berkeley.edu/xlabnews.htm
For more information about the Berkeley Nano-scale Science and Engineering Center visit www.sinam.org/
####
About Berkeley Lab
Berkeley Lab is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory located in Berkeley, California. It conducts unclassified scientific research for DOE’s Office of Science and is managed by the University of California. Visit our Website at www.lbl.gov/
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
(510) 486-5375
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
NEMS
![]() IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
![]() UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
![]() Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
![]() One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








