Home > Press > Plastic antibody works in first tests in living animals
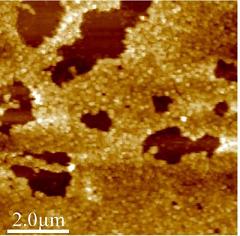 |
| Plastic antibodies, such as this cluster of particles viewed under a powerful microscope, may fight a wide range of human diseases, including viral infections and allergies. Credit: Kenneth Shea |
Abstract:
Scientists are reporting the first evidence that a plastic antibody — an artificial version of the proteins produced by the body's immune system to recognize and fight infections and foreign substances — works in the bloodstream of a living animal.
Plastic antibody works in first tests in living animals
Irvine, CA | Posted on June 16th, 2010The discovery, they suggest in a report in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, is an advance toward medical use of simple plastic particles custom tailored to fight an array of troublesome "antigens." Those antigens include everything from disease-causing viruses and bacteria to the troublesome proteins that cause allergic reactions to plant pollen, house dust, certain foods, poison ivy, bee stings and other substances.
In the report, Kenneth Shea, Yu Hosino, and colleagues refer to previous research in which they developed a method for making plastic nanoparticles, barely 1/50,000th the width of a human hair, that mimic natural antibodies in their ability to latch onto an antigen. That antigen was melittin, the main toxin in bee venom. They make the antibody with molecular imprinting, a process similar to leaving a footprint in wet concrete. The scientists mixed melittin with small molecules called monomers, and then started a chemical reaction that links those building blocks into long chains, and makes them solidify. When the plastic dots hardened, the researchers leached the poison out. That left the nanoparticles with tiny toxin-shaped craters.
Their new research, together with Naoto Oku's group of the University Shizuoka Japan, established that the plastic melittin antibodies worked like natural antibodies. The scientists gave lab mice lethal injections of melittin, which breaks open and kills cells. Animals that then immediately received an injection of the melittin-targeting plastic antibody showed a significantly higher survival rate than those that did not receive the nanoparticles. Such nanoparticles could be fabricated for a variety of targets, Shea says. "This opens the door to serious consideration for these nanoparticles in all applications where antibodies are used," he adds.
"Recognition, Neutralization, and Clearance of Target Peptides in the Bloodstream of Living Mice by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles: A Plastic Antibody"
pubs.acs.org/stoken/presspac/presspac/full/10.1021/ja102148f
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kenneth Shea, Ph.D.
University of California
5042D Frederick Reines Hall
Mail Code: 2025
Irvine, CA 92697
Phone: (949) 824-5844
Yu Hoshino, Ph.D.
University of California, Irvine
5021 Fredrick Reines Hall
Irvine, CA 92697
Phone: (949) 824-2783
Copyright © Eurekalert
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








