Home > Press > Putting the Pedal to the Metal
 |
Abstract:
Lithium metal improves fuel cells
Putting the Pedal to the Metal
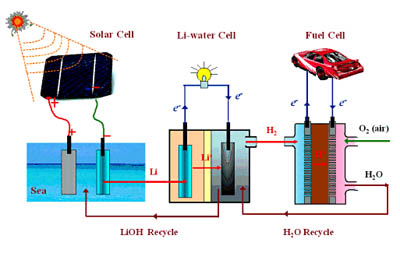
Weinheim, Germany | Posted on May 20th, 2010Water splitting is a clean way to generate hydrogen, which is seen by many as the fuel of the future. Scientists from the Energy Technology Research Institute, AIST in Tsukuba, Japan now report in ChemSusChem on a process that uses chemical energy to generate both hydrogen and electricity. The researchers, headed by Haoshen Zhou, foresee the use of this process in fuel cells for mobile applications.
Powering vehicles and devices with fossil-fuel-based energy is not sustainable, and hydrogen has often been proposed as a way out of the current energy gridlock. However, the production of hydrogen can itself result in large carbon dioxide emissions. One way to avoid this drawback is to make use of the energy of sunlight; first storing the energy in chemical entities, and then releasing the stored energy in straightforward reactions in fuel cells that provide mobile power.
Most people have seen their high-school chemistry teacher demonstrate the violent reaction between sodium and water, in which sodium is reduced. The metals that demonstrate this behavior are part of the alkali metals, which also includes potassium, cesium, and lithium. Dr. Zhou and his team report that by containing the reaction between lithium and water in a closed system two goals can be achieved simultaneously: the chemical reaction produces a current as well as hydrogen, in a controllable manner.
The closed fuel cell system has two compartments separated by a membrane: one compartment contains the lithium (anode) in an organic solvent, while the other contains an aqueous electrolyte solution with an electrode (cathode). Upon reaction a current is produced by electrons from the oxidation of lithium, flowing from the anode to the cathode. When the electrons arrive at the cathode, they reduce water to hydrogen.
Controlling the current also controls the rate of hydrogen generation. Another attractive aspect of this technology is that lithium metal can be produced from salt solutions (e.g., sea water) by using sunlight. In other words, energy from the sun can be "stored" in the metal, and then be used on demand by reacting the lithium in the fuel cell. Recharging the battery would be a matter of replacing the lithium metal cell.
According to Zhou, "Lithium, which is already widely used in various lithium ion batteries and will also be applied in the lithium-air fuel cell and this lithium-water/hydrogen/fuel cell system in the future, may lead humanity to enter a new sustainable lithium society, based on smart grid systems of lithium energy networks." The results demonstrated by the researchers from Tsukuba enable the use of sunlight to eventually produce electricity as well as hydrogen, and can contribute to the further development of a sustainable lifestyle through technology.
Author: Haoshen Zhou, Energy Technology Research Institute, Tsukuba (Japan),
Title: Controllable Hydrogen Generation from Water
ChemSusChem 2010, 3, No. 5, 571-574, Permalink: dx.doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201000049
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Editorial office
Copyright © ChemSusChem
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








