Home > Press > New Nanotech Discovery at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Could Lead to Breakthrough in Infrared Satellite Imaging Technology
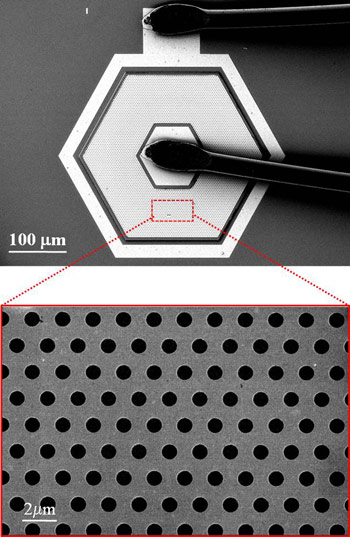 |
| Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Professor Shan-Yu Lin has developed a new nanotechnology-based “microlens” that uses gold to boost the strength of infrared imaging and could lead to a new generation of ultra-powerful satellite cameras and night-vision devices. The device, pictured, leverages the unique properties of nanoscale gold to “squeeze” light into the tiny holes in its surface. |
Abstract:
Researchers Develop Lens-Less, Gold-Covered "Microlens" That Enhances Imaging Signal Without Increasing Noise
New Nanotech Discovery at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Could Lead to Breakthrough in Infrared Satellite Imaging Technology
Troy, NY | Posted on May 19th, 2010Researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed a new nanotechnology-based "microlens" that uses gold to boost the strength of infrared imaging and could lead to a new generation of ultra-powerful satellite cameras and night-vision devices.
By leveraging the unique properties of nanoscale gold to "squeeze" light into tiny holes in the surface of the device, the researchers have doubled the detectivity of a quantum dot-based infrared detector. With some refinements, the researchers expect this new technology should be able to enhance detectivity by up to 20 times.
This study is the first in more than a decade to demonstrate success in enhancing the signal of an infrared detector without also increasing the noise, said project leader Shawn-Yu Lin, professor of physics at Rensselaer and a member of the university's Future Chips Constellation and Smart Lighting Engineering Research Center.
"Infrared detection is a big priority right now, as more effective infrared satellite imaging technology holds the potential to benefit everything from homeland security to monitoring climate change and deforestation," said Lin, who in 2008 created the world's darkest material as well as a coating for solar panels that absorbs 99.9 percent of light from nearly all angles.
"We have shown that you can use nanoscopic gold to focus the light entering an infrared detector, which in turn enhances the absorption of photons and also enhances the capacity of the embedded quantum dots to convert those photons into electrons. This kind of behavior has never been seen before," he said.
Results of the study, titled "A Surface Plasmon Enhanced Infrared Photodetector Based on InAs Quantum Dots," were published online recently by the journal Nano Letters. The paper also will appear in a forthcoming issue of the journal's print edition. The U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research funded this study.
The paper is available online at: pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl100081j
The detectivity of an infrared photodetector is determined by how much signal it receives, divided by the noise it receives. The current state-of-the art in photodetectors is based on mercury-cadmium-telluride (MCT) technology, which has a strong signal but faces several challenges including long exposure times for low-signal imaging. Lin said his new study creates a roadmap for developing quantum dot infrared photodetectors (QDIP) that can outperform MCTs, and bridge the innovation gap that has stunted the progress of infrared technology over the past decade.
The surface plasmon QDIPs are long, flat structures with countless tiny holes on the surface. The solid surface of the structure that Lin built is covered with about 50 nanometers - or 50 billionths of a meter - of gold. Each hole is about 1.6 microns - or 1.6 millionths of a meter - in diameter, and 1 micron deep. The holes are filled with quantum dots, which are nanoscale crystals with unique optical and semiconductor properties.
The interesting properties of the QDIP's gold surface help to focus incoming light directly into the microscale holes and effectively concentrate that light in the pool of quantum dots. This concentration strengthens the interaction between the trapped light and the quantum dots, and in turn strengthens the dots' ability to convert those photons into electrons. The end result is that Lin's device creates an electric field up to 400 percent stronger than the raw energy that enters the QDIP.
The effect is similar to what would result from covering each tiny hole on the QDIP with a lens, but without the extra weight, and minus the hassle and cost of installing and calibrating millions of microscopic lenses, Lin said.
Lin's team also demonstrated in the journal paper that the nanoscale layer of gold on the QDIP does not add any noise or negatively impact the device's response time. Lin plans to continue honing this new technology and use gold to boost the QDIP's detectivity, by both widening the diameter of the surface holes and more effective placement of the quantum dots.
"I think that, within a few years, we will be able to create a gold-based QDIP device with a 20-fold enhancement in signal from what we have today," Lin said. "It's a very reasonable goal, and could open up a whole new range of applications from better night-vision goggles for soldiers to more accurate medical imaging devices."
Co-authors of the paper are Rensselaer Senior Research Scientist James Bur, graduate student Chun-Chieh Chang, and Research Associate Yong-Sung Kim; Yagya D. Sharma, Rajeev V. Shenoi, and Sanjay Krishna of the Center for High Technology Materials at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque; and Danhong Huang of the Space Vehicles Directorate at the Air Force Research Laboratory, Kirtland Air Force Base.
For more information on Lin's research, visit:
www.rpi.edu/dept/phys/faculty/profiles/lin.html
www.rpi.edu/~sylin/
For information on Lin's "darkest material" and solar panel coating visit:
news.rpi.edu/update.do?artcenterkey=2393
www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2008/02/19/AR2008021902617.html
news.rpi.edu/update.do?artcenterkey=2507
www.cnn.com/2008/TECH/science/11/06/solar.coating/index.html
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Mullaney
Phone: (518) 276-6161
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








