Home > Press > Nanobotmodels Company offer vision of future DNA and cell-repair techniques
 |
Abstract:
Five decades of research and practical application of computers in biomedicine has given rise to the discipline of medical informatics, which has made many advances in genomic and translational medicine possible.
Nanobotmodels Company offer vision of future DNA and cell-repair techniques
Ukraine | Posted on March 15th, 2010Developments in nanotechnology and nanorobotics are opening up the prospects for nanomedicine and regenerative medicine where informatics and DNA computing can become the catalysts enabling health care applications at sub-molecular or atomic scales. While nanomedicine promises a new exciting frontier for clinical practice and biomedical research, issues involving cost-effectiveness studies, clinical trials and toxicity assays, drug delivery methods, and the implementation of new personalized therapies still remain challenging.
DNA damage, due to environmental factors and normal metabolic processes inside the cell, occurs at a rate of 1,000 to 1,000,000 molecular lesions per cell per day.
The vast majority of DNA damage affects the primary structure of the double helix; that is, the bases themselves are chemically modified. These modifications can in turn disrupt the molecules' regular helical structure by introducing non-native chemical bonds or bulky adducts that do not fit in the standard double helix. Unlike proteins and RNA, DNA usually lacks tertiary structure and therefore damage or disturbance does not occur at that level.
DNA repair nanorobotics will utilize the same tasks that living systems already prove possible. Access to cells is possible because biologists can stick needles into cells without killing them. Thus, molecular machines are capable of entering the cell.
Also, all specific biochemical interactions show that molecular systems can recognize other molecules by touch, build or rebuild every molecule in a cell, and can disassemble damaged molecules. Finally, cells that replicate prove that molecular systems can assemble every system found in a cell. Therefore, since nature has demonstrated the basic operations needed to perform molecular-level cell repair, in the future, nanomachine based systems will be built that are able to enter cells, sense differences from healthy ones and make modifications to the structure.
The possibilities of these cell repair machines are impressive. Comparable to the size of viruses or bacteria, their compact parts would allow them to be more complex. The early machines will be specialized. As they open and close cell membranes or travel through tissue and enter cells and viruses, machines will only be able to correct a single molecular disorder like DNA damage or enzyme deficiency. Later, cell repair machines will be programmed with more abilities with the help of advanced AI systems. Powerful nanocomputers and fast sequenators will be needed to guide these machines.
These computers will direct machines to examine, take apart, and rebuild damaged molecular structures. Repair machines will be able to repair whole cells by working structure by structure. Then by working cell by cell and tissue by tissue, whole organs can be repaired. Finally, by working organ by organ, health is restored to the body. Cells damaged to the point of inactivity can be repaired because of the ability of molecular machines to build cells from scratch. Therefore, cell repair machines will free medicine from reliance on self repair alone.
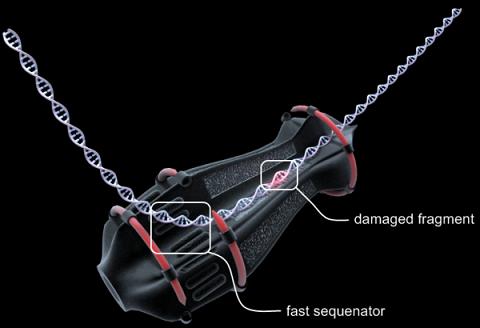
Nanobotmodels Company provides it own vision of DNA-repair cell nanorobots. This type of molecular machine can attach DNA strands and remove damaged fragments from it.
Special express DNA-sequenator analyze all DNA and cut off damaged nucleotides, or unwanted genes.
This model is based on diamondoid nanorobot conception offered by Robert Freitas Jr. Maybe in near future nanorobotic devices will be more sophisticated than today.
Cell repair nanorobotics is young developing part of nanomedicine, so next decade will be decade of DNA reparation using nanotechnology tools.
For more information please visit http://www.nanobotmodels.com/node/47
####
About Nanobotmodels
Our company Nanobotmodels (www.nanobotmodels.com) was founded in 2007 and it goal is develop modern art-science-technology intersections. Nanotechnology boost medicine, engeneering, biotechnology, electronics soon, so artwork and vision of the nanofuture will be very useful.
Our team consist of modern artists, modellers and nanotechnology scientists.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
common questions:
sales and image permissions:
Svidinenko Yuriy, Nanobotmodels Company CEO
Phone: +38 (096) 470 41 66
Copyright © Nanobotmodels
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Artificial Intelligence
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








