Home > Press > Nano imagining takes turn for the better
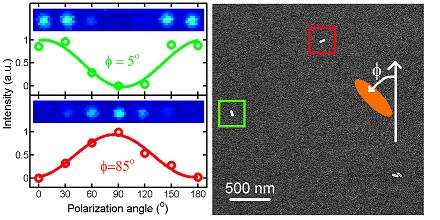 |
| An electron microscope photo from the new paper shows nanorods about 75 nanometers long and 25 nanometers wide on a glass slide at 90-degree angles to each other. An adjacent photothermal image shows them as pixilated smudges. |
Abstract:
Photothermal technique provides new way to track nanoparticles
Nano imagining takes turn for the better
Houston, TX | Posted on February 3rd, 2010Stephan Link wants to understand how nanomaterials align, and his lab's latest work is a step in the right direction.
Link's Rice University group has found a way to use gold nanorods as orientation sensors by combining their plasmonic properties with polarization imaging techniques.
That may make it possible to see and perhaps track single nanoparticles over long periods. It would give researchers new information about materials, including living systems, that incorporate them.
"With a spherical particle, you don't have any information about how it's oriented," said Link, an assistant professor of chemistry and electrical and computer engineering at Rice. "We wanted to see if we could determine the orientation of the nanorods, and eventually we'd like to be able to measure the orientation of the environment they're in. We think this technique could be really useful for that."
Link, primary author Wei-Shun Chang, a Rice research scientist, and their collaborators reported their results this week in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Seeing a single nanoparticle is nothing new. A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) can capture images of particles down to a few nanometers; particles tagged with fluorescent molecules can be seen for as long as the fluorophores are active. Link used this latter method to show nanocars rolling at room temperature last year.
But there are problems with each of those techniques. STMs see nanotubes or quantum dots just fine as long as they're more or less isolated on a conductive surface. But in the wild, the particles would get lost amid the clutter of everything else the microscope sees. And while fluorophores can help pick particles out of the crowd, they can deteriorate in as little as 30 seconds, which limits their usefulness.
Gold nanorods can be "lit up" at will. Lasers at particular wavelengths excite surface plasmons that absorb the energy and emit a heat signature that can be detected by a probe laser. Because plasmons are highly polarized along a nanorod's length, reading the signal while turning the polarization of the laser tells researchers precisely how the rod is oriented.
An electron microscope photo from the new paper shows nanorods about 75 nanometers long and 25 nanometers wide on a glass slide at 90-degree angles to each other. An adjacent photothermal image shows them as pixilated smudges. The smudges are strongest when the laser polarization aligns lengthwise with the nanorods, but they disappear when the laser polarization and rods are 90 degrees out of phase.
"With plasmonics, you always have two properties: absorption and scattering," Link said. "Depending on the size, one or the other dominates. What's unique is that it's now possible to do both on the same structure or do it individually -- so we can only measure absorption or only measure scattering."
Nanorods much smaller than 50 nanometers are not detectable by some scattering methods, Link said, but photothermal detection should work with metallic particles as small as five nanometers; this makes them useful for biological applications. "These gold nanorods are biocompatible. They are not toxic to cells," said Chang, noting their similarity to gold nanoshells currently in human cancer therapy trials based on research by Rice scientists Naomi Halas and Jennifer West.
"Our work is more geared to the fundamentals," Link said of the basic nature of his group's research. "Maybe we can optimize the conditions, and then a physician or somebody who's engineering a probe can take it from there.
"Our place is a little further down the chain of development. I'm happy with that."
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Ji Won Ha and Liane Slaughter. The Robert A. Welch Foundation and 3M supported the work.
View the paper at www.pnas.org/content/early/2010/01/25/0910127107.abstract.
####
About Rice University
Located in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked one of America's best teaching and research universities. Known for its "unconventional wisdom," Rice is distinguished by its: size -- 3,102 undergraduates and 2,237 graduate students; selectivity -- 12 applicants for each place in the freshman class; resources -- an undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio of 5-to-1; sixth largest endowment per student among American private research universities; residential college system, which builds communities that are both close-knit and diverse; and collaborative culture, which crosses disciplines, integrates teaching and research, and intermingles undergraduate and graduate work.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
Associate Director for National Media Relations
Rice University
Direct: 713-348-6327
Cell: 612-702-9473
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








