Home > Press > Unique glass microspheres show promise for medicine, energy
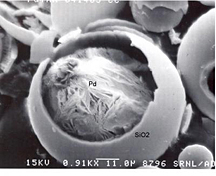 |
| Porous Walled Hollow Glass Microshere |
Abstract:
Networks of interconnected pores in the shells of the Savannah River National Laboratory's Porous Walled Hollow Glass Microspheres give the tiny "microballoons" unique capabilities for potential use in targeted drug delivery, hydrogen storage and other uses.
Unique glass microspheres show promise for medicine, energy
Aiken, SC | Posted on February 1st, 2010Hollow glass microspheres have been used for years in light-weight filler material, insulation, abrasives and other uses. The interconnected pores allow SRNL's unique, patent-pending microspheres to be filled with, hold, and release gases and other materials. Each porous walled hollow glass microsphere is about 50 microns in diameter, about half the width of a human hair. Its walls, which are about 10,000 angstroms thick (an angstrom is one-tenth of one-billionth of a meter) feature pores that range from 100 to 1,000 angstroms, which allow gases and other materials to enter the tiny spheres and be stored or cycled on absorbents inside.
DOE's SRNL originally developed the unique microspheres as a solid-state storage method for hydrogen; they have been successfully demonstrated to store and release the gas.
Work since then has shown potential in other uses, including battery applications and medicine. An article by authors from the Medical College of Georgia and SRNL, which has been accepted for publication in the peer-reviewed journal Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, discusses a possible application for the delivery of anti-cancer drugs.
A licensing agreement with specialty glass provider Mo-Sci Corporation will make the microspheres available for medical R&D and other applications, as well as providing SRNL with a cost-effective supply of the microspheres to continue research and development of additional applications.
Mo-Sci Corporation, a small business entity located in Rolla, Missouri, has been producing specialty glass materials since 1985. They currently produce glass materials to serve a variety of markets ranging from pharmaceutical to health care to space travel and automotive components. SRNL has long been recognized for its expertise in the science and engineering of glass. The laboratory developed the flowsheets and methods used in the Savannah River Site's facility for converting high-level radioactive waste into a stable glass form.
####
About Savannah River National Laboratory
The Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) is the applied research and development laboratory at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Savannah River Site (SRS). The laboratory applies state-of-the-art science to provide practical, high-value, cost-effective solutions to complex technical problems.
The laboratory earns its world-class reputation because of its talented people and their unwavering commitment to safety, security and quality in the delivery of technology solutions that work.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Eric Frickey
803.725.0406,
Copyright © DOE Pulse
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








