Home > Press > Argonne scientists discover mechanism behind superinsulation
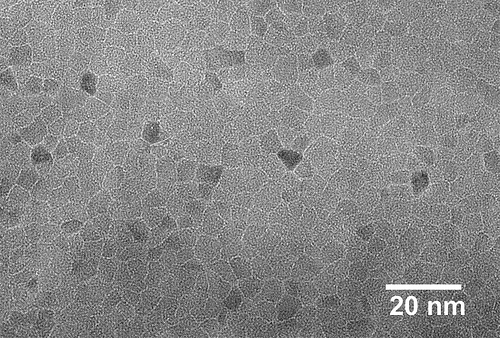 |
| An electron microscopy image of titanium nitride, on which the effect of superinsulation was first observed. Courtesy Argonne National Laboratory. |
Abstract:
Discovery may lead to new types of electronics
Argonne scientists discover mechanism behind superinsulation
Argonne, IL | Posted on December 12th, 2009Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory have discovered the microscopic mechanism behind the phenomenon of superinsulation, the ability of certain materials to completely block the flow of electric current at low temperatures. The essence of the mechanism is what the authors termed "multi-stage energy relaxation."
Traditionally, energy dissipation accompanying current flow is viewed as disadvantageous, as it transforms electricity into heat and thus results in power losses. In arrays of tunnel junctions that are the basic building units of modern electronics, this dissipation permits the generation of current.
Argonne scientist Valerii Vinokour, along with Russian scientists Tatyana Baturina and Nikolai Chtchelkatchev, found that at very low temperatures the energy transfer from tunneling electrons to the thermal environment may occur in several stages.
"First, the passing electrons lose their energy not directly to the heat bath; they transfer their energy to electron-hole plasma, which they generate themselves," Vinokour said. "Then this plasma 'cloud' transforms the acquired energy into the heat. Thus, tunneling current is controlled by the properties of this electron-hole cloud."
As long as the electrons and holes in the plasma cloud are able to move freely, they can serve as a reservoir for energy—but below certain temperatures, electrons and holes become bound into pairs. This does not allow for the transfer of energy from tunneling electrons and impedes the tunneling current, sending the conductivity of the entire system to zero.
"Electron-hole plasma disappears from the game and electrons cannot generate the energy exchange necessary for tunneling," Vinokour said.
Because the current transfer in thin films and granular systems that exhibit superinsulating behavior relies on electron tunneling, the multistage relaxation explains the origin of the superinsulators.
Superinsulation is the opposite of superconductivity; instead of a material that has no resistivity, a superinsulator has a near-infinite resistance. Integration of the two materials may allow for the creation of a new class of quantum electronic devices. This discovery may one day allow researchers to create super-sensitive sensors and other electronic devices.
An earlier paper on the discovery of superinsulation was published in Nature on April 3, 2008. A paper on the mechanism behind superinsulation has been published in Physical Review Letters.
####
About Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America 's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brock Cooper
630/252-5565
Copyright © Argonne National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








