Home > Press > New System for Detection of Single Atoms
 |
Abstract:
Scientists have devised a new technique for real-time detection of freely moving individual neutral atoms that is more than 99.7% accurate and sensitive enough to discern the arrival of a single atom in less than one-millionth of a second, about 20 times faster than the best previous methods.
New System for Detection of Single Atoms
College Park, MD | Posted on December 4th, 2009The system, described in Advance Online Publication at the Nature Physics web site by researchers at the Joint Quantum Institute (JQI) in College Park, MD, and the Universidad de Concepción in Chile, employs a novel means of altering the polarization of laser light trapped between two highly-reflective mirrors, in effect letting the scientists "see" atoms passing through by the individual photons that they scatter.
The ability to detect single atoms and molecules is essential to progress in many areas, including quantum information research, chemical detection and biochemical analysis.
"Existing protocols have been too slow to detect moving atoms, making it difficult to do something to them before they are gone. Our work relaxes that speed constraint," says coauthor David Norris of JQI. "Moreover, it is hard to distinguish between a genuine detection and a random 'false positive' without collecting data over a large period of time. Our system both filters the signal and reduces the detection time."
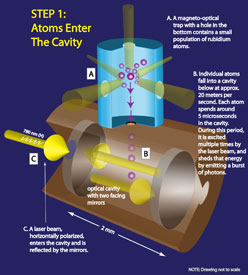
The scientists trap and cool a small population of atoms (rubidium is used in the current experiment) in a vacuum enclosure in such a way that they drop slowly, one at a time, through a hole 1.5 millimeters wide at the bottom of the trap. The atom then falls about 8 centimeters until it enters a tiny chamber, or cavity, that is fitted on opposite sides with highly reflective mirrors that face one another at a distance of about 2 millimeters. Passing through the center of both mirrors is a laser beam of wavelength 780 nanometers - just slightly longer than visible red light. The beam excites the atom as it falls between the mirrors, causing it to reradiate the light in all directions.
That arrangement is a familiar one for labs studying the interaction of atoms and photons. The JQI system, however, has two distinctively unique features.
First, the researchers use two polarizations of cavity light simultaneously: one (horizontal) which is pumped in to efficiently excite the atoms, and the other (vertical) which only appears when emitted by an atom inside the cavity. Although the descent of the atom through the chamber takes only 5 millionths of a second, that is 200 times longer than it takes for the atom to become excited and shed a photon, so this process can happen multiple times before the atom is gone.
Second, they create a magnetic field inside the cavity, which causes the laser light polarization to rotate slightly when an atom is present. Known as the Faraday effect, this phenomenon is typically very weak when observed with a single atom. However, since the light reflecting between the mirrors passes by the atom about 10,000 times, the result is a much larger rotation of a few degrees. This puts significantly more of the laser light into the vertical polarization, making the atoms easier to "see."
The light eventually escapes from the cavity and is fed through a polarizing beamsplitter which routes photons with horizontal polarization to one detector, and vertical polarization to another. Each arriving photon generates a unique time stamp whenever it triggers its detector.
Although the detector for the vertically polarized light should only be sensitive to light coming from an atom in the cavity, it can be fooled occasionally by stray light in the room. But because there are multiple emissions from each atom, there will be a burst of photons whenever an atom passes between the mirrors. This is the signature that the researchers use to confirm an atom detection.
"The chief difficulty lies in verifying that our detector is really sensitive enough to see single atoms, and not just large groups of them," says team leader Luis A. Orozco of JQI. "Fortunately, the statistics of the light serve as a fingerprint for single-atom emission, and we were able to utilize that information in our system."
* "Photon Burst Detection of Single Atoms in an Optical Cavity," M.L. Terraciano, R. Olson Knell, D.G. Norris, J. Jing, A. Fernandez and L.A. Orozco, www.nature.com/nphys/index.html, DOI 10.1038/NPHYS1282.
####
About Joint Quantum Institute, University of Maryland
The Joint Quantum Institute is a research partnership between University of Maryland (UMD) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology, with the support and participation of the Laboratory for Physical Sciences.
Created in 2006 to pursue theoretical and experimental studies of quantum physics in the context of information science and technology, JQI is located on UMD's College Park campus.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
JQI General Info:
Curt Suplee
301.405.2291
or send e-mail to
Copyright © Joint Quantum Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








