Home > Press > Virginia Tech's proposed next generation nano-CT system will enhance nano-scale research
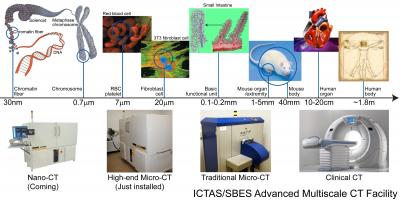 |
| Virginia Tech's advanced multi-scale computed tomography facilities will soon include a Xradia Nano-CT system, and already has a Xradia Micro-CT system, and a Scanco micro-CT system, covering a wide range of image resolutions and sample sizes over six orders of magnitude. The instrumentation is shown on the bottom, and the resulting images are above. Credit: Ge Wang, Virginia Tech |
Abstract:
In 1991, Ge Wang produced the first paper on spiral cone-beam computed tomography (CT), now an imaging technique used in the mainstream of the medical CT field. Today, Wang, known as a pioneer in this field, and his colleagues have been awarded more than $1.3 million from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to develop the next-generation nano-CT imaging system, which promises to greatly reduce the required dose of radiation. Virginia Tech and Xradia, a leading nano-CT company, are also collaborating on the project with a cost-sharing investment of close to $800,000.
Virginia Tech's proposed next generation nano-CT system will enhance nano-scale research
Blacksburg, VA | Posted on September 3rd, 2009CT is an imaging method that shows objects by sections or sectioning, through the use of x-ray waves and computer processing.
"X-ray nano-CT is a cutting edge imaging tool," Wang said, "but a long-standing barrier to realizing its full potential is its inability to precisely reconstruct an interior region of interest within a larger object from purely local projections."
Wang, the Samuel Reynolds Pritchard Professor of Engineering at Virginia Tech, has a scholarly record of achievements in the imaging world. More than 1000 scientific citations are attributed to his group's pioneering efforts. In 2002, for example, he and his research group pioneered another highly sensitive imaging procedure called bioluminescence tomography (BLT). One application of the in vivo molecular imaging technology became the identification of tumors in live animals.
As an additional example, in 2007 he and his collaborators, Yangbo Ye of the University of Iowa and Hengyong Yu, who is the associate director of Wang's CT lab, patented a novel x-ray imaging method called "interior tomography".
Interior tomography, Wang said, was "a first step" towards overcoming the long-standing barrier to realizing the full potential of x-ray nano-CT. Despite the ability of this cutting-edge imaging tool as a non-destructive, non-invasive recorder of information, it cannot "precisely reconstruct an interior region of interest within a large object from purely local projections," Wang said. And, when used in medicine, a patient is subjected to "a radiation dose that must be increased dramatically to obtain improved resolutions."
Wang suggested to the NSF that the combination of X-ray nano-CT and interior tomography will provide "a versatile nano-imaging tool that can visualize fine features within a larger object, and use a much lower radiation dose and in much less time." This new work is the foundation of the NSF project.
Working with Wang on this NSF grant are Chris Wyatt, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering, Linbing Wang, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering, and Yu, all at Virginia Tech. Also, David Carroll, associate professor of physics at Wake Forest University, is a member of the team. On the industrial side, the key collaborators are Steve Wang, S. H. Lau and Wenbing Yun.
Together, they believe they can construct this next generation of a nano-CT imaging system that will provide images that will reveal deeply imbedded details, including subcellular features. And, they believe they can handle a sample that is ten times larger than what is currently available, and at much reduced radiation dose," Wang explained.
Wang, director of the Virginia Tech-Wake Forest University School of Biomedical Engineering Sciences' biomedical imaging division, www.imaging.sbes.vt.edu is also the founding editor-in-chief of the International Journal of Biomedical Imaging. He is the associate editor of the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Transactions on Medical Imaging and others.
SBES is part of the University's Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science (ICTAS). www.ictas.vt.edu/index.shtml. ICTAS has already developed a state-of-the-art nanoscale characterization and fabrication laboratory with capabilities on par with the best nanotechnology labs in the world. With his high-end 500 nanometer micro-CT system, newly funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Wang is making efforts to build an advanced multi-scale CT facility in synergistic combination with the existing university resources as shown in the following chart.
"We are realizing our dream to establish the world's most advanced comprehensive multi-scale and multi-parameter CT facility," Wang said. The use of the facility will be available to other universities and industry.
An academic partnership already exists between Virginia Tech and Xradia. Xradia is already in talks with Virginia Tech about commercializing the next generation nano-CT system. www.xradia.com/
####
About Virginia Tech
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, better known as Virginia Tech, is a public land grant polytechnic university in Blacksburg, Virginia, United States.[2] Virginia Tech is well known for its programs in engineering, architecture, science, business and agriculture.
Founded in 1872 as an agricultural and mechanical college, Virginia Tech continues to be one of the few public universities in the United States which maintains a corps of cadets. The Virginia Tech campus is located in the New River Valley in the Valley and Ridge physiographic region of the Appalachian Mountains in southwestern Virginia, a few miles from the Jefferson National Forest in Montgomery County.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Nystrom
540-231-4371
Copyright © Eurekalert
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








