Home > Press > NIST Develops Novel Ion Trap for Sensing Force and Light
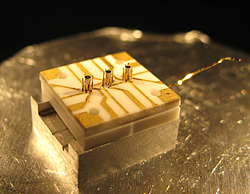 |
| The NIST "stylus trap" can hold a single ion (electrically charged atom) above any of the three sets of concentric cylinders on the centerline. The device could be used as a stylus with a single atom "tip" for sensing very small forces or an interface for efficient transfer of individual light particles for quantum communications. Credit: Maiwald, NIST |
Abstract:
Miniature devices for trapping ions (electrically charged atoms) are common components in atomic clocks and quantum computing research. Now, a novel ion trap geometry demonstrated at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) could usher in a new generation of applications because the device holds promise as a stylus for sensing very small forces or as an interface for efficient transfer of individual light particles for quantum communications.
NIST Develops Novel Ion Trap for Sensing Force and Light
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on July 8th, 2009The "stylus trap," built by physicists from NIST and Germany's University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, is described in Nature Physics.* It uses fairly standard techniques to cool ions with laser light and trap them with electromagnetic fields. But whereas in conventional ion traps, the ions are surrounded by the trapping electrodes, in the stylus trap a single ion is captured above the tip of a set of steel electrodes, forming a point-like probe. The open trap geometry allows unprecedented access to the trapped ion, and the electrodes can be maneuvered close to surfaces. The researchers theoretically modeled and then built several different versions of the trap and characterized them using single magnesium ions.
The new trap, if used to measure forces with the ion as a stylus probe tip, is about one million times more sensitive than an atomic force microscope using a cantilever as a sensor because the ion is lighter in mass and reacts more strongly to small forces. In addition, ions offer combined sensitivity to both electric and magnetic fields or other force fields, producing a more versatile sensor than, for example, neutral atoms or quantum dots. By either scanning the ion trap near a surface or moving a sample near the trap, a user could map out the near-surface electric and magnetic fields. The ion is extremely sensitive to electric fields oscillating at between approximately 100 kilohertz and 10 megahertz.
The new trap also might be placed in the focus of a parabolic (cone-shaped) mirror so that light beams could be focused directly on the ion. Under the right conditions, single photons, particles of light, could be transferred between an optical fiber and the single ion with close to 95 percent efficiency. Efficient atom-fiber interfaces are crucial in long-distance quantum key cryptography (QKD), the best method known for protecting the privacy of a communications channel. In quantum computing research, fluorescent light emitted by ions could be collected with similar efficiency as a read-out signal. The new trap also could be used to compare heating rates of different electrode surfaces, a rapid approach to investigating a long-standing problem in the design of ion-trap quantum computers.
Research on the stylus trap was supported by the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity.
* R. Maiwald, D. Leibfried, J. Britton, J.C. Bergquist, G. Leuchs, and D.J. Wineland. 2009. Stylus ion trap for enhanced access and sensing. Nature Physics, published online June 28.
####
About National Institute of Standards and Technology
From automated teller machines and atomic clocks to mammograms and semiconductors, innumerable products and services rely in some way on technology, measurement, and standards provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Founded in 1901, NIST is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce. NIST's mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Laura Ost
(303) 497-4880
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








