Home > Press > Tubes Grow From Drops
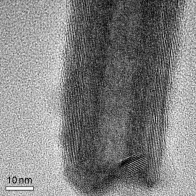 |
| Nanotubes of tin disulfide were fabricated from SnS2 nanoflakes by the vapor-liquid-solid process using bismuth nanodroplets as a catalyst. The SnS2 reagent in the gas phase preferentially adsorbs onto the bismuth particles; upon cooling, nucleation and growth of SnS2 nanotubes occurs (see HRTEM image). Annealing the nanotubes results in the formation of SnS2/SnS superlattices. |
Abstract:
Bismuth-catalyzed growth of tin sulfide nanotubes
Tubes Grow From Drops
Posted on June 15th, 2009Since the discovery of carbon nanotubes in the early 1990s, nanotubes and nanowires have been the focus of much scientific attention. Aside from carbon, nanotubes have since been made from various other materials. Possible applications for these nanostructures range across many fields, including microelectronic circuits, sensors, and special light conductors and light-emitting nanotubes for displays. A research team headed by Wolfgang Tremel at the University of Mainz has now developed a new process for the production of tin sulfide nanotubes. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the researchers let the SnS2 tubes "grow" out of a drop of metal.
Metal sulfides with a lamellar structure that form inorganic nanotubes are not a new concept. They are currently in use in medical technology, for fibers with ultrahigh tensile strength, in hydrogen storage, for rechargeable batteries, in catalysis, and in nanotechnology. One fundamental problem with the fabrication of sulfidic nanotubes is the need for high temperatures to make the planar layers bend and fuse into tubes. In addition, they must be trapped as unstable intermediates. In the case of tin disulfide, this is nearly impossible, however, because the compound decomposes at a significantly lower temperature.
The Mainz researchers thus implemented a different process for the production of tin disulfide nanotubes: they first used a vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) process, a method normally used in the production of semiconducting nanowires. Bismuth metal powder is mixed with tin sulfide nanoflakes and heated in a tube furnace under an argon stream. The reaction product is deposited at the cooler end of the tube.
Nanodroplets of bismuth are formed inside the oven; these act as local points of contact for the tin. In this way, the reaction partners become concentrated within the metal droplet, which then serves as the nucleus for growth of the nanotubes. "In this process, the metal drop is obtained as a sphere at the end of the tube, and the nanotubes grow out of the sphere like a hair out of a follicle," explains Tremel. "Catalysis by the metal droplet makes growth possible at low temperatures."
The new method allowed the scientists to produce nanotubes made of several SnS2 layers with few defects, diameters between 30 and 40 nm, and lengths between 100 and 500 nm.
Author: Wolfgang Tremel, Universitšt Mainz (Germany), www.ak-tremel.chemie.uni-mainz.de/
Title: Bismuth-Catalyzed Growth of SnS2 Nanotubes and Their Stability
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, doi: 10.1002/anie.200900546
####
Copyright © Angewandte Chemie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








