Home > Press > There's safety in nano: search for more nano uses
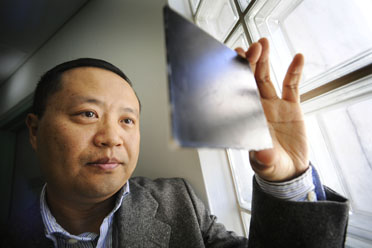 |
| Dr Cheng Yan |
Abstract:
A newly discovered nanocomposite could vastly simplify and enhance the maintenance of large-scale infrastructure such as bridges and aircraft.
There's safety in nano: search for more nano uses
Brisbane, Australia | Posted on May 19th, 2009QUT School of Engineering Systems senior lecturer Dr Cheng Yan said a small piece of the polymer nanocomposite with carbon nanotube fillers could be placed on various surfaces to assist as an early warning system.
"It looks like a piece of thin black sheeting but it can act as a sensor to monitor the strength of infrastructure such as bridges, aircraft, and ships," Dr Yan said.
"Large infrastructure like these must be monitored constantly for cracks, metal fatigue and warping over time so that repairs can be carried out before the damage becomes critical."
Dr Yan said the new nanocomposite sensor was light, strong, easy and cheap to install and more adoptable than many current systems.
"This new material works by monitoring small changes in strain when it is applied to crucial points on a structure such as a bridge or aircraft," he said.
"Maintenance officers can monitor changes in conductivity and can work out the strain applied to the sensor and by catching any deterioration early, save money on maintenance costs.
"It can be also fabricated as a large sensor network attached to the surface of a structure, similar to the neural system in the human body, applying to the detection of car crash and structural health monitoring for various structures."
Dr Yan is one of a team of QUT new material engineers exploring the use of nanotechnology in the creation of new materials for all industries. His recent research also includes making stronger and tougher polymers using various nano-sized fillers.
"We know that substances in their nano form change their properties. As yet we don't fully understand why this is and we are also trying to discover uses for the new properties of various materials," he said.
QUT has joined with the four other universities in the Australian Technology Network (ATN), to establish the ATN-ISTA NanoNetwork with the International Strategic Technology Alliance (ISTA) of universities in China, which has members in more than 20 universities.
The agreement allows QUT nano researchers and those from other ATN universities to partner with Chinese universities in the field of nanotechnology.
####
About Queensland University of Technology
Queensland University of Technology (QUT) is a highly successful Australian university with an applied emphasis in courses and research. Based in Brisbane with a global outlook, it has 40,000 students, including 6000 from overseas (QUT Statistics), and an annual budget of more than AU$500 million.
Contacts:
Media contact: Niki Widdowson, QUT media officer, 07 3138 1841 or
Copyright © Queensland University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








