Home > Press > Shift in Simulation Superiority
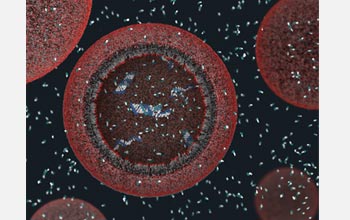 |
| Above is a three-dimensional view of a model protocell approximately 100 nanometers in diameter. The protocell's fatty acid membrane allows nutrients and DNA building blocks to enter the cell and participate in non-enzymatic copying of the cell's DNA. The newly formed strands of DNA remain in the protocell. For more about the computer simulations behind this work, including video and animations, see the press release "A New Way to Think About Earth's First Cells".
Credit: Janet Iwasa, Szostak Laboratory, Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital |
Abstract:
New report highlights strengths and weaknesses in U.S. high-end computer simulations relative to international counterparts
Shift in Simulation Superiority
Arlington, VA | Posted on May 2nd, 2009Science and engineering are advancing rapidly in part due to ever more powerful computer simulations, yet the most advanced supercomputers require programming skills that all too few U.S. researchers possess. At the same time, affordable computers and committed national programs outside the U.S. are eroding American competitiveness in number of simulation-driven fields.
These are some of the key findings in the International Assessment of Research and Development in Simulation-Based Engineering and Science, released on Apr. 22, 2009, by the World Technology Evaluation Center (WTEC).
"The startling news was how quickly our assumptions have to change," said Phillip Westmoreland, program director for combustion, fire and plasma systems at the National Science Foundation (NSF) and one of the sponsors of the report. "Because computer chip speeds aren't increasing, hundreds and thousands of chips are being ganged together, each one with many processors. New ways of programming are necessary."
Like other WTEC studies, this study was led by a team of leading researchers from a range of simulation science and engineering disciplines and involved site visits to research facilities around the world.
The nearly 400-page, multi-agency report highlights several areas in which the U.S. still maintains a competitive edge, including the development of novel algorithms, but also highlights endeavors that are increasingly driven by efforts in Europe or Asia, such as the creation and simulation of new materials from first principles.
"Some of the new high-powered computers are as common as gaming computers, so key breakthroughs and leadership could come from anywhere in the world," added Westmoreland. "Last week's research-directions workshop brought together engineers and scientists from around the country, developing ideas that would keep the U.S. at the vanguard as we face these changes."
Sharon Glotzer of the University of Michigan chaired the panel of experts that executed the studies of the Asian, European and U.S. simulation research activities. Peter Cummings of both Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory co-authored the report with Glotzer and seven other panelists, and the two co-chaired the Apr. 22-23, 2009, workshop with Glotzer that provided agencies initial guidance on strategic directions.
"Progress in simulation-based engineering and science holds great promise for the pervasive advancement of knowledge and understanding through discovery," said Clark Cooper, program director for materials and surface engineering at NSF and also a sponsor of the report. "We expect future developments to continue to enhance prediction and decision making in the presence of uncertainty."
The WTEC study was funded by the National Science Foundation, Department of Defense, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Standards and Technology and the Department of Energy
For more information, read the full report and the University of Michigan press release.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2009, its budget is $9.5 billion, which includes $3.0 billion provided through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to over 1,900 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives about 44,400 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Joshua A. Chamot
NSF
(703) 292-7730
Program Contacts
Clark Cooper
NSF
(703) 292-7899
Phillip R Westmoreland
NSF
(703) 292-8695
Principal Investigators
Sharon Glotzer
University of Michigan
(734) 615-6296
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








