Home > Press > When a good nanoparticle goes bad: Understanding how nanoparticles change form may help solve energy needs
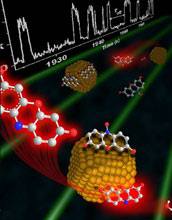 |
| Nanoscale metal particles naturally have a wide variety of shapes and sizes and chemists long suspected that some particles work much better than others when it comes to catalyzing chemical processes. Researchers at Cornell University recently confirmed the hypothesis and discovered that some nanoparticles randomly change from good particles to bad particles.
Credit: Courtesy of Cornell University |
Abstract:
Researchers at Cornell University recently made a major breakthrough when they invented a method to test and demonstrate a long-held hypothesis that some very, very small metal particles work much better than others in various chemical processes such as converting chemical energy to electricity in fuel cells or reducing automobile pollution.
When a good nanoparticle goes bad: Understanding how nanoparticles change form may help solve energy needs
Arlington, VA | Posted on November 10th, 2008The breakthrough, reported in this week's edition of the journal Nature Materials, also came with a surprise. By devising a way to watch individual molecules react with a single nanoscale particle of gold in real time, researchers confirmed that some gold particles are better at increasing the rate of a chemical reaction than others, but they also found that a good catalyst sometimes spontaneously turns bad.
Understanding why these particles change and how to stabilize the "good" particles may lead to solutions for a wide range of problems such as the current global energy challenge.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering, with an annual budget of $6.06 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to over 1,900 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives about 45,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bobbie Mixon
703-292-8485
Program Contacts
Rama Bansil
NSF
(703) 292-8562
Z. Charles Ying
NSF
(703) 292-8428
Thomas P. Rieker
NSF
(703) 292-4914
Principal Investigators
Peng Chen
Cornell University
(607) 254-8533
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








