Home > Press > Team takes first atomic-scale compositional images of fuel-cell nanoparticles
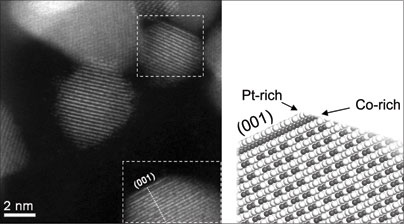 |
| Left image highlights two platinum-cobalt catalyst nanoparticles (inside the dashed boxes) with a 'sandwich' structure of platinum and cobalt atoms near the surface. At right is a cross-sectional model corresponding to the lower particle, showing platinum atoms enriched in the outermost layer, cobalt enriched in the second, and additional layers containing a mixture of the two. (Image at left taken at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.) Image courtesy / Electrochemical Energy Laboratory at MIT |
Abstract:
Work could lead to better catalysts for eco-friendly energy storage devices
Team takes first atomic-scale compositional images of fuel-cell nanoparticles
Cambridge, MA | Posted on October 2nd, 2008In a step toward developing better fuel cells for electric cars and more, engineers at MIT and two other institutions have taken the first images of individual atoms on and near the surface of nanoparticles key to the eco-friendly energy storage devices.
Nanoparticles made of platinum and cobalt are known to catalyze some of the chemical reactions behind fuel cells, making those reactions run up to four times faster than if platinum alone is used as the catalyst.
No one, however, understands exactly why. That's because "little is known about the nanoparticles' surface atomic structure and chemistry," which are key to the particles' activity, said Yang Shao-Horn, an associate professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Department of Materials Science and Engineering and director of the Electrochemical Energy Laboratory at MIT.
Using a new technique known as aberration-corrected Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy, Shao-Horn's team, in collaboration with Professor Paulo Ferreira of the University of Texas at Austin and Dr. Larry Allard of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, identified specific atomic structures near the surface of such a catalyst. That information in hand, the researchers propose a theory for why the material is so active. Perhaps most importantly, "knowing the surface composition will help us design even better catalysts," Shao-Horn said.
The work was reported in the Sept. 24 online issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The researchers analyzed platinum and cobalt nanoparticles that were either treated with acid, or treated with acid then subjected to high heat. Nanoparticles produced both ways are known to be more active than platinum alone. Shao-Horn and colleagues found that each, in turn, also had slightly different surface structures.
For example, in the nanoparticles subjected to heat treatments, the platinum and cobalt atoms formed a "sandwich-like" structure. Platinum atoms covered most of the surface, while the next layer down was composed primarily of cobalt. Successive layers contained mixtures of the two.
The team proposes that these particular nanoparticles are up to four times more active than platinum alone because the platinum atoms on the surface are constrained by the cobalt atoms underneath. "This modifies the interatomic distances between the platinum atoms on the nanoparticle surface," making them more effective in chemical reactions key to fuel cells, Shao-Horn said.
She further noted that "this work bridges the gap between our understanding of electrocatalysis in bulk materials and at the nano-scale."
In addition to Shao-Horn, Allard, and Ferreira, who is also an MIT research affiliate, other members of the research team are Shuo Chen, first author of the paper and a postdoctoral associate in mechanical engineering; Wenchao Sheng, a graduate student in chemistry; and Naoaki Yabuuchi, a research affiliate in mechanical engineering.
The Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation, through its Materials Research Science and Engineering Center program, funded the work.
####
About MIT
The mission of MIT is to advance knowledge and educate students in science, technology, and other areas of scholarship that will best serve the nation and the world in the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Teresa Herbert
MIT News Office
Phone: 617-258-5403
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








