Home > Press > Sol-gel inks produce complex shapes with nanoscale features
 |
| Photo by L. Brian Stauffer
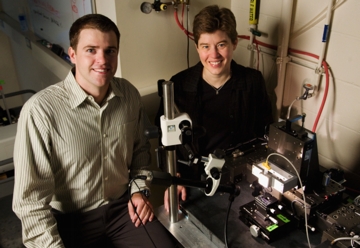
Graduate student Eric Duoss and Jennifer Lewis, the Thurnauer Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, have developed new sol-gel inks that can be printed into patterns to produce three-dimensional structures of metal oxides with nanoscale features. |
Abstract:
New sol-gel inks developed by researchers at the University of Illinois can be printed into patterns to produce three-dimensional structures of metal oxides with nanoscale features.
Sol-gel inks produce complex shapes with nanoscale features
CHAMPAIGN, IL | Posted on October 11th, 2007 The ability to directly pattern functional oxides at the nanoscale opens a new avenue to functional devices. Potential applications include micro-fuel cells, photonic crystals and gas sensors.
The researchers describe the new inks in a paper accepted for publication in the journal Advanced Materials, and featured on its "Advances in Advance" Web site.
"Using this new family of inks, we have produced features as small as 225 nanometers," said co-author Jennifer Lewis, the Thurnauer Professor of Materials Science and Engineering and director of the university's Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory (FSMRL). "Our goal is to get down to 100 nanometer feature sizes."
To create three-dimensional structures, the researchers use a robotic deposition process called direct-write assembly. The concentrated sol-gel ink is dispensed as a filament from a nozzle approximately 1 micron in diameter (about 100 times smaller than a human hair). The ink is dispensed while a computer-controlled micropositioner precisely directs the path. After the pattern for the first layer is complete, the nozzle is raised and another layer is deposited. This process is repeated until the desired shape is produced.
"We have opened direct ink writing to a new realm of functional materials," said graduate student Eric Duoss, the paper's lead author. "Since we print the desired functionality directly, the need for complicated templating and replicating schemes is eliminated."
Unlike previous inks, which require a liquid coagulation reservoir, the newly formulated inks are concentrated enough to rapidly solidify and maintain their shape in air, even as they span gaps in underlying layers.
"This gives us the ability to start, stop and reposition the flow of ink repeatedly, providing exquisite control over the deposition process," Duoss said. "For example, we can directly pattern defects in three-dimensional structures for use as photonic crystals."
After the structures have been assembled, they are converted to the desired functional oxide phase by heating at elevated temperature. Titanium dioxide, which possesses high refractive index and interesting electrical properties, is one material the researchers have successfully produced.
The researchers' ink design and patterning approach can be readily extended to other materials.
"There are a nearly endless variety of materials to choose from," Lewis said. "We envision having a toolbox of inks that can print at the micro- and nanoscale. These inks will be used for heterogeneous integration with other manufacturing techniques to create complex, functional devices composed of many different materials."
In addition to Lewis and Duoss, former post-doctoral researcher Mariusz Twardowski is a co-author of the paper.
Funding was provided by the U.S. Army Research Office. Part of the work was carried out in the FSMRL Center for Microanalysis of Materials, which is partially supported by the U.S. Department of Energy and the U. of I.
Editor's note: To reach Jennifer Lewis, call 217-244-4973; e-mail: .
####
About University of Illinois
At Illinois, research shapes the campus identity, stimulates classroom instruction and serves as a springboard for public engagement activities throughout the world. Opportunities abound for graduate students to develop independent projects and launch their own careers as researchers while working alongside faculty and assisting in their research. Illinois continues its long tradition of groundbreaking accomplishments with remarkable new discoveries and achievements that inspire and enrich the lives of people around the world.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James E. Kloeppel
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1073
Copyright © University of Illinois
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








