Home > Press > Researchers create a new 3D extra-large pore zeolite that opens a new path to the decontamination of water and gas: A team of scientists with the participation of the CSIC develops an extra-large pore silica zeolite from a silicate chain
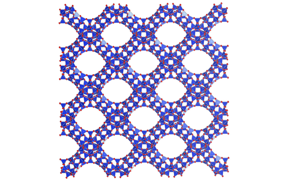 |
| Image of the structure of ZEO-3, a new extra-large pore silica zeolite. / ICMM-CSIC CREDIT ICMM-CSIC |
Abstract:
An international team of researchers with the participation of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has created the most porous stable zeolite known to date, a new pure silica zeolite called ZEO-3. This zeolite was formed by an unprecedented topotactic condensation of a 1D silicate chain to a 3D zeolite. The process is topotactic because the structure of the chain is not altered. It can be applied to remove and recover volatile organic compounds from a gas stream that may even contain water. The discovery, to which scientists from the Institute of Materials Sciences of Madrid (ICMM-CSIC) and the Institute of Nanoscience and Materials of Aragon (INMA-CSIC-UNIZAR) have contributed, is published in the journal Science.
Researchers create a new 3D extra-large pore zeolite that opens a new path to the decontamination of water and gas: A team of scientists with the participation of the CSIC develops an extra-large pore silica zeolite from a silicate chain
Madrid, Spain | Posted on January 20th, 2023Zeolites are microporous silicates that find an ample variety of applications as catalysts, adsorbents, and cation exchangers. Stable silica-based zeolites with increased porosity are in demand to allow adsorption and processing of large molecules, "but challenge our synthetic ability", explains Miguel Camblor, researcher at ICMM and one of the correspondening authors of the research.
As the zeolites pores have are the size of small molecules, there is a limitation on the size of molecules you can process. That is why Zeolites with larger pores "have always been sought" and, specially, those with inpores along 3 dimensions: "because when you have a pore in only one direction, even if it is large, it is easy for it to be blocked, but if you have them in all dimensions, it's difficult,” Camblor points out.
After more than 80 years of extensive international research in this field, this team has created the most porous stable zeolite known so far. "Until now, the zeolites with extra-large pores were not stable, as they were made by germanium instead of siliconm", he says. Previous stable zeolites could reach up to 7 angstroms (1 angstrom is a hundred-millionth of a centimetre).
Last year, this team of researchers published another article in Science about a new zeolite with aluminum and large pores (ZEO-1). Now, the new zeolite has a composition of pure silica. “In both zeolites, ZEO-1 and ZEO-3, there are pores that reach more than 10 angstroms,” says Camblor.
The peculiarities of ZEO-3
This new zeolite has two peculiarities: extra-large pores in all three dimensions and it is formed though the synthesisby calcination of a one-dimensional chain silicate in a topotactic condensation (what means it was made without changes in this chain).
"This had never been seen before," congratules Camblor. "Two-dimensional to three-dimensional topotactic condensations were known, that is, a thing that was lamellar and that by a similar mechanism condensed to give a zeolite, but not from one-dimensional to three-dimensional," he adds.
After the creation of this zeolite the team, with researchers also from Sweden, China and USA, started to experiment its properties: "Since this is a material that is pure silica, it does not have a catalytic capacity, but it has a capacity to absorb very large things. Big organic stuff," says Camblor.
"This zeolite can be applied to remove and recover volatile organic compounds from a gas stream that may even contain water", he explains. "In a site where harmful volatile organic materials are being produced, you can decontaminate and not just remove it but recover itthe contaminant", Camblor ilustrates. With further research this zeolite could be also useful at catalysis and in drug delivery.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Maria Gonzalez
Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
Office: 0034-915-681-819
Ángela R. Bonachera
Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
Copyright © Spanish National Research Council (CSIC)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Zeolites
![]() Dendritic fibrous nanosilica: all-in-one nanomaterial for energy, environment and health November 4th, 2017
Dendritic fibrous nanosilica: all-in-one nanomaterial for energy, environment and health November 4th, 2017
![]() Scientists change properties of zeolites to improve hemodialysis July 29th, 2016
Scientists change properties of zeolites to improve hemodialysis July 29th, 2016
![]() Synthesized microporous 3-D graphene-like carbons: IBS research team create carbon synthesis using zeolites as a template July 1st, 2016
Synthesized microporous 3-D graphene-like carbons: IBS research team create carbon synthesis using zeolites as a template July 1st, 2016
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








