Home > Press > Preserving the goods: A new technique for isolating intact lysosomes from cell cultures: Scientists advance the study of fragile digestive organelles by developing strategy to rapidly extract them from cells using magnetic nanoparticles
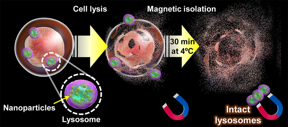 |
| Once magnetic nanoparticles have naturally accumulated in a cell’s lysosomes through the endocytic pathway, the cell membrane is ruptured. and its contents “sifted” for 30 minutes using magnets. At the end of this process, intact lysosomes can be retrieved from the magnets and used to study their structure, metabolites, and protein composition. CREDIT Shinya Maenosono from JAIST. |
Abstract:
The correct functioning of our cells rests upon the precise orchestration of many complex processes and organelles. Lysosomes—vital cell organelles—are enzyme-filled subunits found within many animal cells that help break down and reuse macromolecules, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleotides. Besides their function in cellular digestion and waste management, lysosomes also participate in amino acid signaling, which stimulates protein synthesis alongside other effects.
Preserving the goods: A new technique for isolating intact lysosomes from cell cultures: Scientists advance the study of fragile digestive organelles by developing strategy to rapidly extract them from cells using magnetic nanoparticles
Ishikawa, Japan | Posted on January 7th, 2022Given that a lot of diseases are caused by defects in lysosome function, it is no surprise that researchers have been actively trying to understand these organelles for decades. But there are only a few techniques that allow the extraction of lysosomes from within a cell. The most common method is called “density gradient ultracentrifugation.” It involves gently breaking the cell membrane and applying a centrifugal force to the cell’s contents. This separates the cell components by density. Unfortunately, some other organelles have the same density as lysosomes, resulting in samples with impurities. Moreover, the process takes so long that by the time it finishes, many lysosomal proteins have already been lost and/or degraded.
A more advanced technique, called “immunoprecipitation,” relies on modifying the surface proteins of lysosomes so that they can be captured by magnetic beads covered in specially tailored antibodies. While this approach produces purer results, the protein composition of the extracted lysosomes is modified by the procedure and, thus, subsequent protein analyses can be compromised. It is clear, then, that we need to find a better way to extract lysosomes from cells.
Fortunately, a team of scientists led by Prof. Shinya Maenosono from the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) has stepped up to the plate and developed a novel strategy to quickly separate intact lysosomes with high purity. This study was published in ACS Nano and also included Prof. Kazuaki Matsumura and Associate Prof. Yuichi Hiratsuka from JAIST, and Prof. Tomohiko Taguchi of Tohoku University, Japan.
Their strategy is centered around the use of magnetic-plasmonic hybrid nanoparticles (MPNPs) made of silver and an iron–cobalt alloy and covered in a compound called amino dextran (aDxt). The basis for this approach is that the aDxt-covered MPNPs are naturally ingested by the cells through “endocytosis,” which culminates inside lysosomes. Once enough MPNPs have accumulated inside the lysosomes, the cells can be gently “crushed,” and the lysosomes retrieved using magnets.
For this method to work, it is essential that MPNPs are located only within lysosomes and not in other organelles. This is where plasmon imaging comes in handy, as the distinct way plasmonic nanoparticles interact with light makes them easy to visualize with an optical microscope. By coloring each type of organelle in the endocytic pathway differently using immunostaining and checking how the location of MPNPs overlaps with them, the researchers determined the precise time it takes most MPNPs to reach the lysosomes. In turn, this ensures that the separation process yields lysosome samples with high purity.
Afterwards, the team analyzed the effects of temperature and magnetic separation time on the protein composition of the extracted lysosomes. Their results showed that protein loss was remarkably quick, even at temperatures as low as 4°C. Fortunately, their approach was fast enough to extract intact lysosomes, as Prof. Maenosono highlights: “We found that the maximum time required to isolate lysosomes after cell rupture was 30 minutes, which is substantially shorter than the time required using centrifugation-based techniques, which typical require a minimum separation time of several hours.”
Overall, this new technique will help researchers explore the fragile metabolites of lysosomes and how they change in response to stimuli. In turn, this shall pave the way to new insights into disorders related to lysosomal dysfunction. In this regard, Prof. Maenosono remarks: “Given the profound relation of lysosomes with many cellular metabolites, a deeper understanding of lysosomal function is necessary to determine its regulation in different cell states. Therefore, our technique can contribute to better understanding and treatment of lysosomal diseases in the future.” Moreover, this new approach could be modified to extract other organelles besides lysosomes. Hopefully, this study will put us closer to understanding the contents of cells to a much higher degree.
####
About Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST)
Founded in 1990 in Ishikawa prefecture, the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) was the first independent national graduate school in Japan. Now, after 30 years of steady progress, JAIST has become one of Japan’s top-ranking universities. JAIST counts with multiple satellite campuses and strives to foster capable leaders with a state-of-the-art education system where diversity is key; about 40% of its alumni are international students. The university has a unique style of graduate education based on a carefully designed coursework-oriented curriculum to ensure that its students have a solid foundation on which to carry out cutting-edge research. JAIST also works closely both with local and overseas communities by promoting industry–academia collaborative research.
About Professor Shinya Maenosono from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Japan
Shinya Maenosono received a PhD in Chemical Systems Engineering from the University of Tokyo, Japan, in 2002. He then joined the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) as an Associate Professor in 2006. In 2012, he became a full Professor at JAIST, where he leads a research group. His research in JAIST has focused on the wet chemical synthesis of semiconductor nanoparticles with controlled size, shape, and composition for applications in energy conversion devices, as well as the synthesis and bioapplication of monometallic and alloyed multimetallic nanoparticles. He has published over 120 papers and 12 book chapters.
Funding information
This study was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant no. 21K14506)
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Shinya Maenosono
Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +81-761-51-1611
Copyright © Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Plasmonics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
![]() A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
![]() Patterning silicon at the one nanometer scale: Scientists engineer materials’ electrical and optical properties with plasmon engineering August 13th, 2021
Patterning silicon at the one nanometer scale: Scientists engineer materials’ electrical and optical properties with plasmon engineering August 13th, 2021
![]() TPU scientists offer new plasmon energy-based method to remove CO2 from atmosphere March 19th, 2021
TPU scientists offer new plasmon energy-based method to remove CO2 from atmosphere March 19th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








