Home > Press > Graphene-Adsorbate van der Waals bonding memory inspires 'smart' graphene sensors
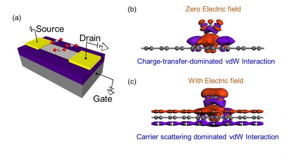 |
| (a) Adsorbed CO2 molecules on graphene sensor (b) van der Waals (vdW) interaction between adsorbed molecules and graphene at zero electric field (c) vdW interaction between adsorbed molecules and graphene with electric field. CREDIT JAIST |
Abstract:
Monolayer graphene, an atomic-layer thick sheet of carbon has found immense applications in diverse fields including chemical sensors, detecting single molecule adsorption events electronically. Therefore, monitoring physisorbed molecule induced changes of the electrical response of graphene has become ubiquitous in graphene based sensors. Electric field tuning of the physisorbed molecule-graphene interaction results in enhanced gas sensing due to unique electric field dependent charge-transfer between the adsorbed gas and graphene. Molecular identification in graphene sensors was predicted based on this unique electrically tunable charge-transfer, which is a signature for different adsorbed molecules. Nevertheless, to achieve molecular identification functionality in graphene sensors, an understanding of the gas adsorption/desorption events and retention of the graphene-gas molecule interaction after turning off the electric field is desired. Until now, the graphene-gas molecule bonding interactions were considered randomized by ambience thermal energy after the electric field is turned off, which is not surprising since these interactions are van der Waals (vdW) bonding and so inherently weak. Nevertheless, this assumed thermal randomization of the graphene-gas molecule vdW bonding was unverified experimentally and a major drawback towards electrically tunable charge-transfer based molecular identification in graphene gas sensors.
Graphene-Adsorbate van der Waals bonding memory inspires 'smart' graphene sensors
Ishikawa, Japan | Posted on July 17th, 2020To clarify the bonding retention of adsorbed gas molecules on graphene with and without electric field tuning, Osazuwa Gabriel Agbonlahor (current doctoral student), Tomonori Imamura (graduated master's student), Dr. Manoharan Murugananthan (Senior Lecturer), and Professor Hiroshi Mizuta of Mizuta Laboratory at the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) monitored the time-dependent vdW interaction decay of adsorbed CO2 molecules on graphene at different electric fields. Using the electric field to tune the interaction between the adsorbed gas and graphene, the charge-transfer between the adsorbed CO2 molecules and graphene was monitored while the tuning electric field was turned on and after it was turned off. Remarkably, the graphene-gas molecule van der Waals interactions were retained hours after the electric field was turned off, demonstrating both charge-transfer and carrier scattering retention characteristic of the previously applied electric field magnitude and direction i.e. the adsorbed CO2 molecules demonstrated a 'vdW bonding memory'. Due to this bonding memory, the charge-transfer and scattering properties of the adsorbed gas molecules on graphene can be studied hours after the electric field is turned off which is critical for identifying adsorbed molecules based on their signature charge-transfer response to an applied electric field. Furthermore, the long bonding retention time (over 2h) of these electrically tuned adsorbed molecules, sets graphene-based sensors apart as platforms for developing 'smart' sensors suitable for 'beyond-sensing' applications in memory devices and conformational switches.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hiroshi Mizuta
81-076-151-1571
Copyright © Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








