Home > Press > Researchers discover new boron-lanthanide nanostructure
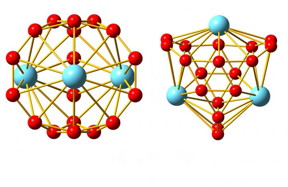 |
| The family of boron-based nanostructures has a new member: metallo-borospherenes, hollow cages made from 18 boron atoms and three atoms of lanthanide elements. CREDIT Wang Lab / Brown University |
Abstract:
The discovery of carbon nanostructures like two-dimensional graphene and soccer ball-shaped buckyballs helped to launch a nanotechnology revolution. In recent years, researchers from Brown University and elsewhere have shown that boron, carbon's neighbor on the periodic table, can make interesting nanostructures too, including two-dimensional borophene and a buckyball-like hollow cage structure called borospherene.
Researchers discover new boron-lanthanide nanostructure
Providence, RI | Posted on June 25th, 2020Now, researchers from Brown and Tsinghua University have added another boron nanostructure to the list. In a paper published in Nature Communications, they show that clusters of 18 boron atoms and three atoms of lanthanide elements form a bizarre cage-like structure unlike anything they've ever seen.
"This is just not a type of structure you expect to see in chemistry," said Lai-Sheng Wang, a professor of chemistry at Brown and the study's senior author. "When we wrote the paper we really struggled to describe it. It's basically a spherical trihedron. Normally you can't have a closed three-dimensional structure with only three sides, but since it's spherical, it works."
The researchers are hopeful that the nanostructure may shed light on the bulk structure and chemical bonding behavior of boron lanthanides, an important class of materials widely used in electronics and other applications. The nanostructure by itself may have interesting properties as well, the researchers say.
"Lanthanide elements are important magnetic materials, each with very different magnetic moments," Wang said. "We think any of the lanthanides will make this structure, so they could have very interesting magnetic properties."
Wang and his students created the lanthanide-boron clusters by focusing a powerful laser onto a solid target made of a mixture of boron and a lanthanide element. The clusters are formed upon cooling of the vaporized atoms. Then they used a technique called photoelectron spectroscopy to study the electronic properties of the clusters. The technique involves zapping clusters of atoms with another high-powered laser. Each zap knocks an electron out of the cluster. By measuring the kinetic energies of those freed electrons, researchers can create a spectrum of binding energies for the electrons that bond the cluster together.
"When we see a simple, beautiful spectrum, we know there's a beautiful structure behind it," Wang said.
To figure out what that structure looks like, Wang compared the photoelectron spectra with theoretical calculations done by Professor Jun Li and his students from Tsinghua. Once they find a theoretical structure with a binding spectrum that matches the experiment, they know they've found the right structure.
"This structure was something we never would have predicted," Wang said. "That's the value of combining theoretical calculation with experimental data."
Wang and his colleagues have dubbed the new structures metallo-borospherenes, and they're hopeful that further research will reveal their properties.
###
Other co-authors on the paper were Teng-Teng Chen, Wan-Lu Li, Wei-Jia Chen, Xiao-Hu Yu, Xin-Ran Dong. The research was supported by National Science Foundation (CHE-1763380) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (21590792, 91426302 and 21433005).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Stacey
401-863-3766
@brownuniversity
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








