Home > Press > Self-assembling, biomimetic composites possess unusual electrical properties
 |
| Biomimetic composites are produced by topological interactions, expanding the limits of the physical properties, such as electrical conductivity. CREDIT Mert Vural, Penn State |
Abstract:
Sometimes, breaking rules is not a bad thing. Especially when the rules are apparent laws of nature that apply in bulk material, but other forces appear in the nanoscale.
Self-assembling, biomimetic composites possess unusual electrical properties
University Park, PA | Posted on June 4th, 2020"Nature knows how to go from the small, atomic scale to larger scales," said Melik Demirel, professor of engineering science and mechanics and holder of the Lloyd and Dorothy Foehr Huck Chair in Biomimetic Materials. "Engineers have used mixing rules to enhance properties, but have been limited to a single scale. We've never gone down to the next level of hierarchical engineering. The key challenge is that there are apparent forces at different scales from molecules to bulk."
Composites, by definition, are composed of more than one component. Mixture rules say that, while the ratios of one component to another can vary, there is a limit on the physical properties of the composite. According to Demirel, his team has broken that limit, at least on the nanoscale.
"If you have a conducting polymer composite the amounts of polymer and metal compound are limited by the rule of mixtures," said Demirel. "The rules govern everything about the matrix and filler. We took materials -- a biopolymer and an atomically thin conducting material -- let them organize by self assembly, and broke the rule of mixtures."
The team's materials are composed of a biomimetic polymer based on tandem repeat proteins produced by gene duplication and inspired by the structure of squid ring teeth proteins, and conducting titanium carbide 2D MXene, an only a few-molecules-thick layer of metal. This layered composite self-assembles and the polymer mediates the distance between the metal layers. By using genetic engineering of tandem repeat proteins -- a biopolymer that repeats a conserved sequence -- the researchers can control the inter-layer distance of conducting layers without changing the composite fractions. The researchers' goal is to create self-assembling materials with unprecedented control over their physical properties using synthetic biology.
Because the polymer self-assembles into a cross-linked network, the matrix-to-filler ratios in tiny areas can break the mixture rules, and the electrical properties of the layered material changes. The researchers report the results of their work in a recent issue of ACS Nano.
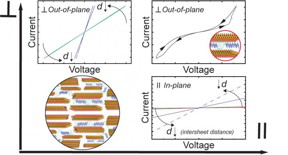
This biomimetic polymer metal composite can be both flexible and conductive in the proper bulk mixtures. On the microscopic scale, when the structural symmetry is broken, electrical conductivity depends on direction.
"What is unique is that now you can get in-plane electrical conductivity that differs from out-of-plane conductivity," said Demirel.
As long as the current is going along the plane of the 2D material layers, the conductivity is linear, but if the current is directed across the layers, the conductivity becomes nonlinear.
"Now we can make a storage device," said Demirel. "We could also make diodes, switches, regulators and other electronic devices. We want to make materials that are designed with desired properties for building novel functionalities, which are difficult to achieve or previously unattainable."
###
Also working on this project from Penn State are Haoyue Zhu and Huihun Jung, postdoctoral fellows in engineering science and mechanics; and Benjamin D. Allen, research associate. Other researchers on the project were Mert Vural, postdoctoral fellow at Linköping University in Sweden and formerly a postdoctoral fellow at Penn State, and Abdon Pena-Francesch, soon to be a Penn State doctoral graduate and an assistant professor at the University of Michigan.
The Army Research Office and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research basic science programs supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-5689
@penn_state
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








