Home > Press > Maryland engineers open door to big new library of tiny nanoparticles: A new study expands the landscape of nanomaterials -- and what we can do with them
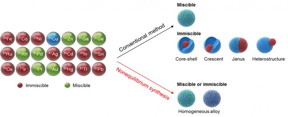 |
| Via conventional bimetallic synthesis methods, only readily miscible metals (shown in green) can mix with Cu while others (shown in red) form phase-segregated structures (such as core-shell). In contrast, via the non-equilibrium synthesis, Cu and other metals can be kinetically trapped in homogeneously mixed nanoparticles, regardless of their thermodynamic miscibility. CREDIT Yang et al. |
Abstract:
The development of bimetallic nanoparticles (i.e., tiny particles composed of two different metals that exhibit several new and improved properties) represents a novel area of research with a wide range of potential applications. Now, a research team in the University of Maryland (UMD)'s A. James Clark School of Engineering has developed a new method for mixing metals generally known to be immiscible, or unmixable, at the nanoscale to create a new range of bimetallic materials. Such a library will be useful for studying the role of these bimetallic particles in various reaction scenarios such as the transformation of carbon dioxide to fuel and chemicals.
Maryland engineers open door to big new library of tiny nanoparticles: A new study expands the landscape of nanomaterials -- and what we can do with them
College Park, MD | Posted on April 24th, 2020The study, led by Professor Liangbing Hu, was published in Science Advances on April 24, 2020. Research Associate Chunpeng Yang served as first author on the study.
"With this method, we can quickly develop different bimetallics using various elements, but with the same structure and morphology," said Hu. "Then we can use them to screen catalytic materials for a reaction; such materials will not be limited by synthesizing difficulties."
The complex nature of nanostructured bimetallic particles makes mixing such particles using conventional methods difficult, for a variety of reasons - including the chemical makeup of the metals, particle size, and how metals arrange themselves at the nanoscale.
This new non-equilibrium synthesis method exposes copper-based mixes to a thermal shock of approximately 1300 degrees Celsius for .02 seconds and then rapidly cools them to room temperature. The goal of using such a short interval of thermal heat is to quickly trap, or 'freeze,' the high-temperature metal atoms at room temperature while maintaining their mixing state. In doing so, the research team was able to prepare a collection of homogeneous copper-based alloys. Typically, copper only mixes with a few other metals, such as zinc and palladium - but by using this new method, the team broadened the miscible range to include copper with nickel, iron, and silver, as well.
"Using a scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope, we were able to confirm the morphology - how the materials formed - and size of the resulting Cu-Ag [copper-silver] bimetallic nanoparticles," Yang said.
This method will enable scientists to create more diverse nanoparticle systems, structures, and materials having applications in catalysis, biological applications, optical applications, and magnetic materials.
As a model system for rapid catalyst development, the team investigated copper-based alloys as catalysts for carbon monoxide reduction reactions, in collaboration with Feng Jiao, professor at the University of Delaware. The electro-catalysis of carbon monoxide reduction (COR) is an attractive platform, allowing scientists to use greenhouse gas and renewable electrical energy to produce fuels and chemicals.
"Copper is, thus far, the most promising monometallic electrocatalyst that drives carbon monoxide reduction to value-added chemicals," said Jiao. "The ability to rapidly synthesize a wide variety of copper-based bimetallic nanoalloys with a uniform structure enables us to conduct fundamental studies on the structure-property relationship in COR and other catalyst systems."
The non-equilibrium synthetic strategy can be extended to other bimetallic or metal oxide systems, too. Utilizing artificial intelligence-based machine learning, the new synthetic method will make rapid catalyst screening and rational design possible.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Melissa L. Andreychek
301-405-0292
@UMDRightNow
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








