Home > Press > 3D hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst helps efficiently reduce CO2? This new catalyst will bring CO2 one step closer to serving as a sustainable energy source
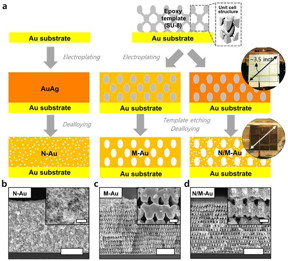 |
| Fabrication procedures of various gold nanostructures through proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) and electroplating techniques. CREDIT Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh, KAIST |
Abstract:
KAIST researchers developed a three-dimensional (3D) hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst with carbon dioxide (CO2) to carbon monoxide (CO) conversion rate up to 3.96 times higher than that of conventional nanoporous gold catalysts. This new catalyst helps overcome the existing limitations of the mass transport that has been a major cause of decreases in the CO2 conversion rate, holding a strong promise for the large-scale and cost-effective electrochemical conversion of CO2 into useful chemicals.
3D hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst helps efficiently reduce CO2? This new catalyst will bring CO2 one step closer to serving as a sustainable energy source
Ulsan, Korea | Posted on March 13th, 2020As CO2 emissions increase and fossil fuels deplete globally, reducing and converting CO2 to clean energy electrochemically has attracted a great deal of attention as a promising technology. Especially due to the fact that the CO2 reduction reaction occurs competitively with hydrogen evolution reactions (HER) at similar redox potentials, the development of an efficient electrocatalyst for selective and robust CO2 reduction reactions has remained a key technological issue.
Gold (Au) is one of the most commonly used catalysts in CO2 reduction reactions, but the high cost and scarcity of Au pose obstacles for mass commercial applications. The development of nanostructures has been extensively studied as a potential approach to improving the selectivity for target products and maximizing the number of active stable sites, thus enhancing the energy efficiency.
However, the nanopores of the previously reported complex nanostructures were easily blocked by gaseous CO bubbles during aqueous reactions. The CO bubbles hindered mass transport of the reactants through the electrolyte, resulting in low CO2 conversion rates.
In the study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS) on March 4, a research group at KAIST led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering designed a 3D hierarchically porous Au nanostructure with two different sizes of macropores and nanopores. The team used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) and electroplating techniques that are effective for fabricating the 3D well-ordered nanostructures.
The proposed nanostructure, comprised of interconnected macroporous channels 200 to 300 nanometers (nm) wide and 10 nm nanopores, induces efficient mass transport through the interconnected macroporous channels as well as high selectivity by producing highly active stable sites from numerous nanopores.
As a result, its electrodes show a high CO selectivity of 85.8% at a low overpotential of 0.264 V and efficient mass activity that is up to 3.96 times higher than that of de-alloyed nanoporous Au electrodes.
"These results are expected to solve the problem of mass transfer in the field of similar electrochemical reactions and can be applied to a wide range of green energy applications for the efficient utilization of electrocatalysts," said the researchers.
###
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Younghye Cho
82-423-502-294
@KAISTPR
Copyright © UNIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








