Home > Press > The power of going small: Copper oxide subnanoparticle catalysts prove most superior
 |
| A research concept:Subnano copper oxide particles for solvent-free aerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons |
Abstract:
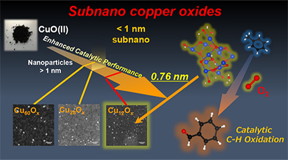
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology have shown that copper oxide particles on the sub-nanoscale are more powerful catalysts than those on the nanoscale. These subnanoparticles can also catalyze the oxidation reactions of aromatic hydrocarbons far more effectively than catalysts currently used in industry. This study paves the way to better and more efficient utilization of aromatic hydrocarbons, which are important materials for both research and industry.
The power of going small: Copper oxide subnanoparticle catalysts prove most superior
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on February 11th, 2020The selective oxidation of hydrocarbons is important in many chemical reactions and industrial processes, and as such, scientists have been on the lookout for more efficient ways to carry out this oxidation. Copper oxide (CunOx) nanoparticles have been found useful as a catalyst for processing aromatic hydrocarbons, but the quest of even more effective compounds has continued.
In the recent past, scientists applied noble metal-based catalysts comprising of particles at the sub-nano level. At this level, particles measure less than a nanometer and when placed on appropriate substrates, they can offer even higher surface areas than nanoparticle catalysts to promote reactivity.
In this trend, a team of scientists including Prof. Kimihisa Yamamoto and Dr. Makoto Tanabe from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) investigated chemical reactions catalyzed by CunOx subnanoparticles (SNPs) to evaluate their performance in the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons. CunOx SNPs of three specific sizes (with 12, 28, and 60 copper atoms) were produced within tree-like frameworks called dendrimers (Fig. 2). Supported on a zirconia substrate, they were applied to the aerobic oxidation of an organic compound with an aromatic benzene ring.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) were used to analyze the synthesized SNPs' structures, and the results were supported by density functionality theory (DFT) calculations.
The XPS analysis and DFT calculations revealed increasing ionicity of the copper–oxygen (Cu–O) bonds as SNP size decreased. This bond polarization was greater than that seen in bulk Cu–O bonds, and the greater polarization was the cause of the enhanced catalytic activity of the CunOx SNPs.
Tanabe and the team members observed that the CunOx SNPs sped up the oxidation of the CH3 groups attached to the aromatic ring, thereby leading to the formation of products. When the CunOx SNP catalyst was not used, no products were formed. The catalyst with the smallest CunOx SNPs, Cu12Ox, had the best catalytic performance and proved to be the longest lasting.
As Tanabe explains, "the enhancement of the ionicity of the Cu–O bonds with decrease in size of the CunOx SNPs enables their better catalytic activity for aromatic hydrocarbon oxidations."
Their research supports the contention that there is great potential for using copper oxide SNPs as catalysts in industrial applications. "The catalytic performance and mechanism of these size-controlled synthesized CunOx SNPs would be better than those of noble metal catalysts, which are most commonly used in industry at present," Yamamoto say, hinting at what CunOx SNPs can achieve in the future.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Further Information
Specially Appointed Associate Professor Makoto Tanabe
Hybrid Materials Unit
Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tel +81-45-924-5260
Professor Kimihisa Yamamoto
Hybrid Materials Unit
Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science
Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tel +81-45-924-5873
Contact
Public Relations Section, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tel +81-3-5734-2975
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








