Home > Press > A new method to study lithium dendrites could lead to better, safer batteries
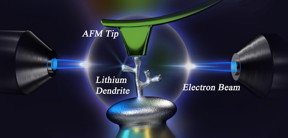 |
| A lithium dendrite is imaged and stress-tested under an atomic force microscope tip. CREDIT Zhang Lab/Penn State |
Abstract:
Lithium ion batteries often grow needle-like structures between electrodes that can short out the batteries and sometimes cause fires. Now, an international team of researchers has found a way to grow and observe these structures to understand ways to stop or prevent their appearance.
A new method to study lithium dendrites could lead to better, safer batteries
University Park, PA | Posted on January 10th, 2020"It is difficult to detect the nucleation of such a whisker and observe its growth because it is tiny," said Sulin Zhang, professor of mechanical engineering, Penn State. "The extremely high reactivity of lithium also makes it very difficult to experimentally examine its existence and measure its properties."
Lithium whiskers and dendrites are needle-like structures only a few hundred nanometers in thickness that can grow from the lithium electrode through either liquid or solid electrolytes toward the positive electrode, shorting out the battery and sometimes causing fire.
The collaborative team from China, Georgia Tech and Penn State successfully grew lithium whiskers inside an environmental transmission electron microscope (ETEM) using a carbon dioxide atmosphere. The reaction of carbon dioxide with lithium forms an oxide layer that helps stabilize the whiskers.
They report their results online this week in Nature Nanotechnology. The paper is "Revealing the growth and stress generation of lithium whiskers by in situ ETEM-AFM."
Innovatively, the team used an atomic force microscope (AFM) tip as a counter electrode and the integrated ETEM-AFM technique allows simultaneous imaging of the whisker growth and measurement of the growth stress. If the growth stress is too high, it would penetrate and fracture the solid electrolyte and allow the whiskers to continue growing and eventually short-circuit the cell.
"Now that we know the limit of the growth stress, we can engineer the solid electrolytes accordingly to prevent it," Zhang said. Lithium metal-based all-solid-state batteries are desirable because of greater safety and higher energy density.
This new technique will be welcomed by the mechanics and electrochemistry communities and be useful in many other applications, Zhang said.
Next up for the team is to look at the dendrite as it forms against a more realistic solid-state electrolyte under TEM to see exactly what happens.
###
The researchers are from Yanshan University, China University of Petroleum and Xiangtan University, all in China; and Ting Zhu of Georgia Tech.
The National Key Research and Development Program of China, Beijing Natural Science Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and several additional Chinese foundations, supported this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-5689
@penn_state
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








