Home > Press > Growing carbon nanotubes with the right twist: Researchers synthetize nanotubes with a specific structure expanding previous theories on carbon nanotube growth
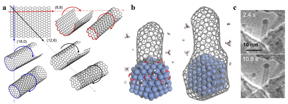 |
| (a) Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) could be viewed as single-atom layer thick graphene sheets rolled into a cylinder. Different directions of rolling determine CNTs' properties. (b) Schematic diagram showing a carbon nanotube's lifetime during chemical vapor deposition synthesis. Transition metals (blue structure) serve as catalysts, critical to elongate the CNT (left), until the carbon concentration on the catalyst surface becomes so abundant that the nanoparticle gets encapsulated by graphitic or amorphous carbon, forming a "cap" at the end of the cylinder and ending the growth of the CNT (right). (c) Environmental transmission electron microscope images of a CNT taken at different times during growth. The CNT contains a cobalt nanoparticle on its top end, a typical feature of tip-growth. CREDIT IBS |
Abstract:
In a recently published paper in Science Advances, Feng Ding of the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials, within the Institute of Basic Science (IBS, South Korea) and colleagues, have achieved the creation of a specific type of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with a selectivity of 90%, and expanded the current theory that explains the synthesis of these promising nano-cylinders.
Growing carbon nanotubes with the right twist: Researchers synthetize nanotubes with a specific structure expanding previous theories on carbon nanotube growth
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on December 13th, 2019CNTs are incredibly strong and light nanomaterials made of carbon with superior current carrying capacity and very high thermal conductivity, making them ideal for electronic applications. Although CNTs are considered as some of the most interesting materials for the future, scientists are still struggling for their controllable synthesis.
The CNTs' shape can be compared to paper tubes: in the same way as a cylinder can be created by rolling a sheet of paper, so CNTs can be imagined as a single layer of graphite rolled up on itself. Similarly, as different tubes can be produced by rolling a paper around its long side, its short side, or diagonally at different angles. Depending on the rolling direction, a graphite layer can produce different CNT structures, some are conducting and others are semiconducting, thus selectively creating a specific type of CNT will be key for their future use, such as building energy efficient computer chips. However, CNTs are not produced by rolling, but are grown nanometer after nanometer, adding carbon at the rim of nano-cylinders, one atom at a time. Despite various studies during the last three decades, the understanding on CNT growth remains very limited and rational experimental design for the growth of specific types of CNTs is challenging.
One of the most promising manufacturing methods for CNT is the chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In this process, metal nanoparticles combined with carbon-containing gases form CNTs inside a high-temperature furnace. On the tip of the tubes, the metal nanoparticles play a critical role as catalysts: they dissociate the carbon source from the gases, and assist the attachment of these carbon atoms to the CNT wall, making the tubes longer and longer. The growth of the CNT terminates once the catalyst particle is encapsulated by graphitic or amorphous carbon.
Carbon atoms are inserted onto the interface between a growing CNT and a catalyst nanoparticle, in active sites of the rim, and are available to incorporate new atoms. A previous model of CNT's growth rate showed that the latter is proportional to the density of these active sites at the interface between CNT and the catalyst, or the specific structure of the CNT.
In this study, the researchers monitored the steady growth of CNTs on a magnesium oxide (MgO) support with carbon monoxide (CO) as the carbon feedstock and cobalt nanoparticles as catalysts at 700oC. The direct experimental measurements of 16 CNTs showed how to expand the previous theory. "It was surprising that the growth rate of a carbon nanotubes only depends on the size of the catalyst particle. This implies that our previous understanding on carbon nanotubes growth was not complete," says Maoshuai He, the first author of the paper.
More specifically, carbon atoms that are deposited on the catalyst particle surface can be either incorporated on the active side of the CNT or removed by etching agents, such as H2, H2O, O2, or CO2. To explain the new experimental observations, the team included the effects of carbon insertion and removal during CNT growth and discovered that the growth rate depends on the catalyst's surface area and tube diameter ratio.
"Compared to the previous model, we added three more factors: the rate of precursor deposition, the rate of carbon removal by etching agents, and the rate of carbon insertion into a carbon nanotube wall. When feedstock dissociation cannot be balanced by carbon etching, the rate of carbon nanotube growth will no longer depend on the structure of the carbon nanotube. On the other hand, the previous theory is still valid if the etching is dominating," explains Ding, a group leader of the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials.
Interestingly, the new theory of CNT growth leads to a new mechanism to selectively grow a specific type of CNTs, denoted as (2n, n) CNTs, which is characterized by the maximum number of active sites at the interface between the CNT and the catalyst. This CNT structure would correspond to rolling a sheet of graphite diagonally at an angle of around 19 degrees.
"If there is no carbon etching and the carbon nanotubes growth is slow, carbon atoms on the catalyst surface will accumulate," says Jin Zhang, co-author of the study and professor of Peking University, China. "This may lead to the formation of graphitic or amorphous carbon, which are established mechanisms of carbon nanotube growth termination. In this case, only carbon nanotubes which are able to add carbon atoms on their walls, that is with the highest number of active sites, can survive."
Guided by the new theoretical understanding, the researchers were able to design experiments that produced (2n, n) CNTs with a selectivity of up to 90%: the highest selective growth of this type of CNT was achieved in the absence of any etching agent and with a high feedstock concentration.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dahee Carol Kim
82-428-788-133
@IBS_media
Copyright © Institute of Basic Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








