Home > Press > Researchers embrace imperfection to improve biomolecule transport
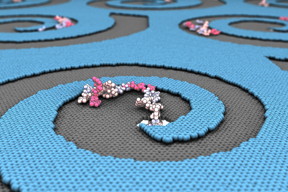 |
| Laboratory-engineered membrane defects with edges that spiral downward would give biomolecules like DNA, RNA and proteins no other option than to sink into a nanopore for delivery, sorting and analysis. Graphic courtesy Manish Shankla |
Abstract:
While watching the production of porous membranes used for DNA sorting and sequencing, University of Illinois researchers wondered how tiny steplike defects formed during fabrication could be used to improve molecule transport. They found that the defects – formed by overlapping layers of membrane – make a big difference in how molecules move along a membrane surface. Instead of trying to fix these flaws, the team set out to use them to help direct molecules into the membrane pores.
DNA on graphene steps
Force-guided delivery of DNA molecule to a nanopore
Researchers embrace imperfection to improve biomolecule transport
Champaign, IL | Posted on August 8th, 2019Their findings are published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Nanopore membranes have generated interest in biomedical research because they help researchers investigate individual molecules – atom by atom – by pulling them through pores for physical and chemical characterization. This technology could ultimately lead to devices that can quickly sequence DNA, RNA or proteins for personalized medicine.
“Molecular dynamics simulations let us watch what is happening while simultaneously measuring how much force is required to get the molecule to clear a step,” Aksimentiev said. “We were surprised to find that it takes less force to move a molecule down a step than up. Although it may seem intuitive that gravity would make stepping down easier, it is not the case here because gravity is negligible at the nanoscale, and the force required to move up or down should be the same.”
Aksimentiev said team members originally thought they could use concentric defect patterns that form around the pores to force the molecules down, but their simulations showed the molecules congregating along the edges of the steps. That is when it dawned on them: A defect with edges that spiral into a pore, combined with an applied directional force, would give the molecule no other option than to go into the pore – kind of like a drain.
“This way, we can drop molecules anywhere on the membrane covered with these spiral structures and then pull the molecules into a pore,” he said.
The researchers have not yet produced a membrane with spiral defects in the laboratory, but that task may be easier than trying to rid a graphene membrane of the current molecule-immobilizing step defects, they said.
“When manufactured at scale, defect-guided capture may potentially increase the DNA capture throughput by several orders of magnitude, compared with current technology,” Shankla said.
“After a long development process, we are excited to see this principle used in a variety of other materials and applications such as delivery of individual molecules to reaction chambers for experiments,” the researchers said.
The National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation and the Dutch Research Council supported this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
LOIS YOKSOULIAN
PHYSICAL SCIENCES EDITOR
217-244-2788
Aleksei Aksimentiev
217-333-6495
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








