Home > Press > Transforming biology to design next-generation computers, using a surprise ingredient: Purdue University researchers turned to biology to help in the design of next-generation computers
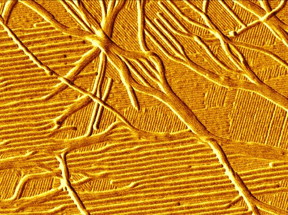 |
| A Purdue University group has found ways of transforming structures that occur naturally in cell membranes to create other architectures, like parallel 1nm-wide line segments, more applicable to computing. CREDIT Purdue University/Shelley Claridge |
Abstract:
Moore's law - which says the number of components that could be etched onto the surface of a silicon wafer would double every two years - has been the subject of recent debate. The quicker pace of computing advancements in the past decade have led some experts to say Moore's law, the brainchild of Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in the 1960s, no longer applies. Particularly of concern, next-generation computing devices require features smaller than 10 nanometers - driving unsustainable increases in fabrication costs.
Transforming biology to design next-generation computers, using a surprise ingredient: Purdue University researchers turned to biology to help in the design of next-generation computers
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on July 25th, 2019Biology creates features at sub-10nm scales routinely, but they are often structured in ways that are not useful for applications like computing. A Purdue University group has found ways of transforming structures that occur naturally in cell membranes to create other architectures, like parallel 1nm-wide line segments, more applicable to computing.
Inspired by biological cell membranes, Purdue researchers in the Claridge Research Group have developed surfaces that act as molecular-scale blueprints for unpacking and aligning nanoscale components for next-generation computers. The secret ingredient? Water, in tiny amounts.
"Biology has an amazing tool kit for embedding chemical information in a surface," said Shelley Claridge, a recently tenured faculty member in chemistry and biomedical engineering at Purdue, who leads a group of nanomaterials researchers. "What we're finding is that these instructions can become even more powerful in nonbiological settings, where water is scarce."
In work just published in Chem, sister journal to Cell, the group has found that stripes of lipids can unpack and order flexible gold nanowires with diameters of just 2 nm, over areas corresponding to many millions of molecules in the template surface.
"The real surprise was the importance of water," Claridge said. "Your body is mostly water, so the molecules in your cell membranes depend on it to function. Even after we transform the membrane structure in a way that's very nonbiological and dry it out, these molecules can pull enough water out of dry winter air to do their job."
Their work aligns with Purdue's Giant Leaps celebration, celebrating the global advancements in sustainability as part of Purdue's 150th anniversary. Sustainability is one of the four themes of the yearlong celebration's Ideas Festival, designed to showcase Purdue as an intellectual center solving real-world issues.
The research team is working with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent their work. They are looking for partners for continued research and to take the technology to market.
####
About Purdue University
About Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization operates one of the most comprehensive technology transfer programs among leading research universities in the U.S. Services provided by this office support the economic development initiatives of Purdue University and benefit the university's academic activities through commercializing, licensing and protecting Purdue intellectual property. The office is managed by the Purdue Research Foundation, which received the 2016 Innovation and Economic Prosperity Universities Award for Innovation from the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. For more information on licensing a Purdue innovation, contact the Office of Technology Commercialization at For more information about funding and investment opportunities in startups based on a Purdue innovation, contact the Purdue Foundry at Purdue Research Foundation is a private, nonprofit foundation created to advance the mission of Purdue University.
Purdue Research Foundation contact: Chris Adam, 765-588-3341,
Source: Shelley Claridge,
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chris Adam
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Organic Electronics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








