Home > Press > Artificial photosynthesis transforms carbon dioxide into liquefiable fuels
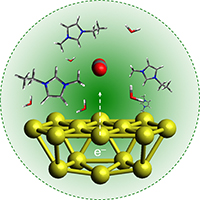 |
| Under green light and assisted by an ionic liquid, gold nanoparticles, bottom, lend electrons to convert CO2 molecules, the red and grey spheres in the center, to more complex hydrocarbon fuel molecules. Graphic courtesy Sungju Yu, Jain Lab at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign |
Abstract:
Chemists at the University of Illinois have successfully produced fuels using water, carbon dioxide and visible light through artificial photosynthesis. By converting carbon dioxide into more complex molecules like propane, green energy technology is now one step closer to using excess CO2 to store solar energy – in the form of chemical bonds – for use when the sun is not shining and in times of peak demand.
Artificial photosynthesis transforms carbon dioxide into liquefiable fuels
Champaign, IL | Posted on May 22nd, 2019Plants use sunlight to drive chemical reactions between water and CO2 to create and store solar energy in the form of energy-dense glucose. In the new study, the researchers developed an artificial process that uses the same green light portion of the visible light spectrum used by plants during natural photosynthesis to convert CO2 and water into fuel, in conjunction with electron-rich gold nanoparticles that serve as a catalyst. The new findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
“The goal here is to produce complex, liquefiable hydrocarbons from excess CO2 and other sustainable resources such as sunlight,” said Prashant Jain, a chemistry professor and co-author of the study. “Liquid fuels are ideal because they are easier, safer and more economical to transport than gas and, because they are made from long-chain molecules, contain more bonds – meaning they pack energy more densely.”
In Jain’s lab, Sungju Yu, a postdoctoral researcher and first author of the study, uses metal catalysts to absorb green light and transfer electrons and protons needed for chemical reactions between CO2 and water – filling the role of the pigment chlorophyll in natural photosynthesis.
Gold nanoparticles work particularly well as a catalyst, Jain said, because their surfaces interact favorably with the CO2 molecules, are efficient at absorbing light and do not break down or degrade like other metals that can tarnish easily.
There are several ways in which the energy stored in bonds of the hydrocarbon fuel is freed. However, the easy conventional method of combustion ends up producing more CO2 – which is counterproductive to the notion of harvesting and storing solar energy in the first place, Jain said.
“There are other, more unconventional potential uses from the hydrocarbons created from this process,” he said. “They could be used to power fuel cells for producing electrical current and voltage. There are labs across the world trying to figure out how the hydrocarbon-to-electricity conversion can be conducted efficiently,” Jain said.
As exciting as the development of this CO2-to-liquid fuel may be for green energy technology, the researchers acknowledge that Jain’s artificial photosynthesis process is nowhere near as efficient as it is in plants.
“We need to learn how to tune the catalyst to increase the efficiency of the chemical reactions,” he said. “Then we can start the hard work of determining how to go about scaling up the process. And, like any unconventional energy technology, there will be many economic feasibility questions to be answered, as well.”
The Energy and Biosciences Institute, through the EBI-Shell program, supported this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
LOIS YOKSOULIAN
PHYSICAL SCIENCES EDITOR
217-244-2788
Prashant Jain
217-333-3417
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








