Home > Press > A hole in one for holographic display: Tiny pinholes in a thin film could pave the way for more widespread applications for 3D holographic displays
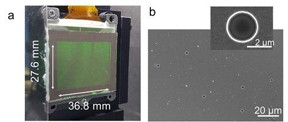 |
| The actual 3D holographic display, and an electron microscope image of the non-periodic pinholes. CREDIT KAIST |
Abstract:
Researchers in Korea have designed an ultrathin display that can project dynamic, multi-colored, 3D holographic images, according to a study published in Nature Communications.
A hole in one for holographic display: Tiny pinholes in a thin film could pave the way for more widespread applications for 3D holographic displays
Daejeon, Korea | Posted on April 19th, 2019The system's critical component is a thin film of titanium filled with tiny holes that precisely correspond with each pixel in a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel. This film acts as a 'photon sieve' - each pinhole diffracts light emerging from them widely, resulting in a high-definition 3D image observable from a wide angle.
The entire system is very small: they used a 1.8-inch off-the-shelf LCD panel with a resolution of 1024 x 768. The titanium film, attached to the back of the panel, is a mere 300 nanometres thick.
"Our approach suggests that holographic displays could be projected from thin devices, like a cell phone," says Professor YongKeun Park, a physicist at KAIST who led the research. The team demonstrated their approach by producing a hologram of a moving, tri-coloured cube.
Specifically, the images are made by pointing differently coloured laser beams made of parallel light rays at the small LCD panel. The photon sieve has a hole for each pixel in the LCD panel. The holes are precisely positioned to correspond to the pixel's active area. The pinholes diffract the light emerging from them, producing 3D images.
Previous studies from Professor Park's group have used optical diffusors for the same purpose, but the size of the device was bulky and difficult to be operated, and it took a long period of time to calibrate. In the present work, on the other hand, tailored their photon sieve to demonstrate a simple, compact and scalable method for 3D holographic display. This technique can be readily applied to existing LCD displays.
Applications for holograms have been limited by cumbersome techniques, high computation requirements, and poor image quality. Improving current techniques could lead to a wide variety of applications, including 3D cinema viewing without the need for glasses, watching holographic videos on television and smart phone screens.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Younghye Cho
82-423-502-294
Copyright © Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








