Home > Press > Hybrid material may outperform graphene in several applications: A structure comprising a molybdenum disulfide monolayer on an azobenzene substrate could be used to build a highly compactable and malleable quasi-two-dimensional transistor powered by light
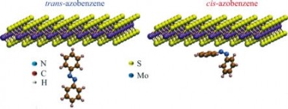 |
| A structure comprising a molybdenum disulfide monolayer on an azobenzene substrate could be used to build a highly compactable and malleable quasi-two-dimensional transistor powered by light (image: atomistic representations of molybdenum disulfide monolayer with an azobenzene molecule in its trans and cis isomers/ Physical Review B) |
Abstract:
Materials that are hybrid constructions (combining organic and inorganic precursors) and quasi-two-dimensional (with malleable and highly compactable molecular structures) are on the rise in several technological applications, such as the fabrication of ever-smaller optoelectronic devices.
Hybrid material may outperform graphene in several applications: A structure comprising a molybdenum disulfide monolayer on an azobenzene substrate could be used to build a highly compactable and malleable quasi-two-dimensional transistor powered by light
São Paulo City, Brazil | Posted on February 28th, 2019An article published in the journal Physical Review B describes a study in this field resulting from the doctoral research of Diana Meneses Gustin and Luís Cabral, both supervised by Victor Lopez Richard, a professor at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in Brazil. Cabral was co-supervised by Juarez Lopes Ferreira da Silva, a professor at the University of São Paulo's São Carlos Chemistry Institute (IQSC-USP). Gustin was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP via a doctoral scholarship and a scholarship for a research internship abroad.
"Gustin and Cabral explain theoretically the unique optical and transport properties resulting from interaction between a molybdenum disulfide monolayer [inorganic substance MoS2] and a substrate of azobenzene [organic substance C12H10N2]," Lopez Richard told.
Illumination makes the azobenzene molecule switch isomerization and transition from a stable trans spatial configuration to a metastable cis form, producing effects on the electron cloud in the molybdenum disulfide monolayer. These effects, which are reversible, had previously been investigated experimentally by Emanuela Margapoti in postdoctoral research conducted at UFSCar and supported by FAPESP.
Gustin and Cabral developed a model to emulate the process theoretically. "They performed ab initio simulations [computational simulations using only established science] and calculations based on density functional theory [a quantum mechanical method used to investigate the dynamics of many-body systems]. They also modeled the transport properties of the molybdenum disulfide monolayer when disturbed by variations in the azobenzene substrate," Richard explained.
While the published paper does not address technological applications, the deployment of the effect to build a light-activated two-dimensional transistor is on the researchers' horizon.
"The quasi two-dimensional structure makes molybdenum disulfide as attractive as graphene in terms of space reduction and malleability, but it has virtues that potentially make it even better. It's a semiconductor with similar electrical conductivity properties to graphene's and it's more versatile optically because it emits light in the wavelength range from infrared to the visible region," Richard said.
The hybrid molybdenum-disulfide-azobenzene structure is considered a highly promising material, but a great deal of research and development will be required if it is to be effectively deployed in useful devices.
####
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at http://www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at http://www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe .
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Joao Carlos Silva
55-113-838-4381
Copyright © São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








