Home > Press > Static electricity could charge our electronics: While common in everyday life, the science behind this phenomenon is not well understood
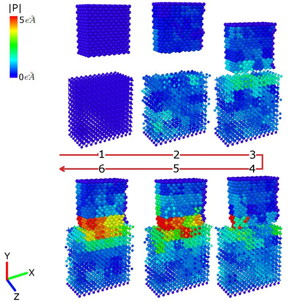 |
| These images show how the surfaces of magnesia (top block) and barium titanate (bottom block) respond when they come into contact. The resulting lattice deformations in each object contributes to the driving force behind the electric charge transfer during friction. CREDIT Credit: James Chen, University at Buffalo. |
Abstract:
Unhappy with the life of your smartphone battery?
Thought so.
Help could be on the way from one of the most common, yet poorly understand, forms of power generation: static electricity.
Static electricity could charge our electronics: While common in everyday life, the science behind this phenomenon is not well understood
Buffalo, NY | Posted on January 25th, 2019"Nearly everyone has zapped their finger on a doorknob or seen child's hair stick to a balloon. To incorporate this energy into our electronics, we must better understand the driving forces behind it," says James Chen, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at the University at Buffalo.
Chen is a co-author of a study in the December issue of the Journal of Electrostatics that suggests the cause of this hair-raising phenomenon is tiny structural changes that occur at the surface of materials when they come into contact with each other.
The finding could ultimately help technology companies create more sustainable and longer-lasting power sources for small electronic devices.
Supported by a $400,000 National Science Foundation grant, Chen and Zayd Leseman, PhD, associate professor of mechanical and nuclear engineering at Kansas State University, are conducting research on the triboelectric effect, a phenomenon wherein one material becomes electrically charged after it contacts a different material through friction.
The triboelectric effect has been known since ancient times, but the tools for understanding and applying it have only become available recently due to the advent of nanotechnology.
"The idea our study presents directly answers this ancient mystery, and it has the potential to unify the existing theory. The numerical results are consistent with the published experimental observations," says Chen.
The research Chen and Leseman conduct is a mix of disciplines, including contact mechanics, solid mechanics, materials science, electrical engineering and manufacturing. With computer models and physical experiments, they are engineering triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs), which are capable of controlling and harvesting static electricity.
"The friction between your fingers and your smartphone screen. The friction between your wrist and smartwatch. Even the friction between your shoe and the ground. These are great potential sources of energy that we can to tap into," Chen says. "Ultimately, this research can increase our economic security and help society by reducing our need for conventional sources of power."
As part of the grant, Chen has worked with UB undergraduate students, as well as high school students at the Health Sciences Charter School in Buffalo, to promote science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) education.
###
This study was made available online in September 2018 ahead of final publication in December 2018.
Funding for the award runs until 2020, and Chen says more findings will be presented at the American Physical Society's meeting in March in Boston, Massachusetts.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Cory Nealon
716-645-4614
Copyright © University at Buffalo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








