Home > Press > New insight into molecular processes
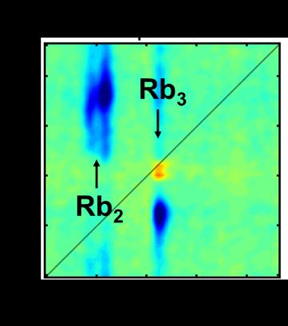 |
| 2D-spectroscopy illustrates the light-induced reactions of Rubidium molecules in various color spectrums. CREDIT Illustration: Lukas Bruder |
Abstract:
A research team headed by Prof. Dr. Frank Stienkemeier and Dr. Lukas Bruder of the University of Freiburg's Institute of Physics has succeeded for the first time in applying 2D-spectroscopy to isolated molecular systems and thus in tracing the interactive processes at a molecular level more precisely. The team has published its results in the science journal "Nature Communications".
New insight into molecular processes
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on November 23rd, 2018Behind every natural process are processes at atomic and molecular levels. These often take place on very short time scales, often they are faster than a billionth of a second and are based on the interplay of many factors. Until now this has made it difficult to unencrypt the precise microscopic mechanisms such as the conversion of energy in photovoltaics or photosynthesis.
In this area of research coherent two-dimensional spectroscopy has been established, which involves ultra-short laser pulses being shot at the matter. This method has enabled researchers to follow the dynamics of corresponding processes, once the matter has absorbed the light. Two-dimensional spectroscopy provides a far greater amount of information than other methods, combined with a high time resolution in the range of femtoseconds - a femtosecond is the millionth part of a billionth of a second. However, for technical reasons, this method had until now been restricted to studying bulk liquid or solid material. "In previous experiments the samples were very complex, which made it extremely difficult to isolate individual quantum-mechanical effects and study them precisely. Our approach overcomes this hurdle," explains Bruder, who headed the experiment.
In preparation for the experiment, the scientists produced superfluid helium droplets, which have no friction, in an ultrahigh vacuum. The droplets are only a few nanometers in size and serve as a substrate in which the researchers synthesize the actual molecular structures using a modular principle, in other words by combining molecular components one by one. These structures are then studied by means of 2D-spectroscopy. "In the experiments we combined various specific technologies which drastically improved the measurement sensitivity of the 2D-spectroscopy. Only by doing this was it possible for us to study isolated molecules," explains Bruder.
In an initial study, the Freiburg scientists produced extremely cold molecules of the chemical element Rubidium in an unusual quantum state, whereby the atoms of the molecule are only weakly bonded, and analyzed their light-induced reactions under the influence of the helium environment. "Our approach opens up a range of applications, specifically in the field of photovoltaics or optoelectronics, and will eventually contribute to a better understanding of fundamental processes," says Stienkemeier.
###
The 2D-spectroscopy research project was funded as part of the International Graduate School "CoCo", which was established by the German Research Foundation, and the "COCONIS" project of the European Research Council (ERC).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Frank Stienkemeier
49-761-203-7609
Copyright © University of Freiburg
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








