Home > Press > Nanotubes may give the world better batteries: Rice U. scientists' method quenches lithium metal dendrites in batteries that charge faster, last longer
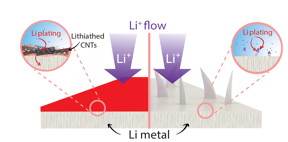 |
| An illustration shows how lithium metal anode developed at Rice University are protected from dendrite growth by a film of carbon nanotubes. (Credit: Tour Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Rice University scientists are counting on films of carbon nanotubes to make high-powered, fast-charging lithium metal batteries a logical replacement for common lithium-ion batteries.
Nanotubes may give the world better batteries: Rice U. scientists' method quenches lithium metal dendrites in batteries that charge faster, last longer
Houston, TX | Posted on October 25th, 2018The Rice lab of chemist James Tour showed thin nanotube films effectively stop dendrites that grow naturally from unprotected lithium metal anodes in batteries. Over time, these tentacle-like dendrites can pierce the battery's electrolyte core and reach the cathode, causing the battery to fail.
That problem has both dampened the use of lithium metal in commercial applications and encouraged researchers worldwide to solve it.
Lithium metal charges much faster and holds about 10 times more energy by volume than the lithium-ion electrodes found in just about every electronic device, including cellphones and electric cars.
"One of the ways to slow dendrites in lithium-ion batteries is to limit how fast they charge," Tour said. "People don't like that. They want to be able to charge their batteries quickly."
The Rice team's answer, detailed in Advanced Materials, is simple, inexpensive and highly effective at stopping dendrite growth, Tour said.
"What we've done turns out to be really easy," he said. "You just coat a lithium metal foil with a multiwalled carbon nanotube film. The lithium dopes the nanotube film, which turns from black to red, and the film in turn diffuses the lithium ions."
"Physical contact with lithium metal reduces the nanotube film, but balances it by adding lithium ions," said Rice postdoctoral researcher Rodrigo Salvatierra, co-lead author of the paper with graduate student Gladys López-Silva. "The ions distribute themselves throughout the nanotube film."
When the battery is in use, the film discharges stored ions and the underlying lithium anode refills it, maintaining the film's ability to stop dendrite growth.
The tangled-nanotube film effectively quenched dendrites over 580 charge/discharge cycles of a test battery with a sulfurized-carbon cathode the lab developed in previous experiments. The researchers reported the full lithium metal cells retained 99.8 percent of their coulombic efficiency, the measure of how well electrons move within an electrochemical system.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice alumni Almaz Jalilov of the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Saudi Arabia; Jongwon Yoon, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute; and Gang Wu, an instructor, and Ah-Lim Tsai, a professor of hematology, both at the McGovern Medical School at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Institutes of Health, the National Council of Science and Technology, Mexico; the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel, Brazil; and Celgard, LLC.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,970 undergraduates and 2,934 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








