Home > Press > Graphene carpets: So neurons communicate better: Research by SISSA reveals that graphene can strengthen neuronal activity, confirming the unique properties of this nanomaterial. The study has been published on Nature Nanotechnology
 |
Abstract:
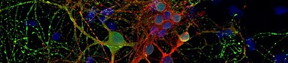
A work led by SISSA and published on Nature Nanotechnology reports for the first time experimentally the phenomenon of ion 'trapping' by graphene carpets and its effect on the communication between neurons. The researchers have observed an increase in the activity of nerve cells grown on a single layer of graphene. Combining theoretical and experimental approaches they have shown that the phenomenon is due to the ability of the material to 'trap' several ions present in the surrounding environment on its surface, modulating its composition. Graphene is the thinnest bi-dimensional material available today, characterised by incredible properties of conductivity, flexibility and transparency. Although there are great expectations for its applications in the biomedical field, only very few works have analysed its interactions with neuronal tissue.
Graphene carpets: So neurons communicate better: Research by SISSA reveals that graphene can strengthen neuronal activity, confirming the unique properties of this nanomaterial. The study has been published on Nature Nanotechnology
Trieste, Italy | Posted on June 13th, 2018A study conducted by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, in association with the University of Antwerp (Belgium), the University of Trieste and the Institute of Science and Technology of Barcelona (Spain), has analysed the behaviour of neurons grown on a single layer of graphene, observing a strengthening in their activity. Through theoretical and experimental approaches the researchers have shown that such behaviour is due to reduced ion mobility, in particular of potassium, to the neuron-graphene interface. This phenomenon is commonly called 'ion trapping', already known at theoretical level, but observed experimentally for the first time only now. "It is as if graphene behaves as an ultra-thin magnet on whose surface some of the potassium ions present in the extra cellular solution between the cells and the graphene remain trapped. It is this small variation that determines the increase in neuronal excitability" comments Denis Scaini, researcher at SISSA who has led the research alongside Laura Ballerini.
The study has also shown that this strengthening occurs when the graphene itself is supported by an insulator, like glass, or suspended in solution, while it disappears when lying on a conductor. "Graphene is a highly conductive material which could potentially be used to coat any surface. Understanding how its behaviour varies according to the substratum on which it is laid is essential for its future applications, above all in the neurological field" continues Scaini, "considering the unique properties of graphene it is natural to think for example about the development of innovative electrodes of cerebral stimulation or visual devices".
It is a study with a double outcome. Laura Ballerini comments as follows: "This 'ion trap' effect was described only in theory. Studying the impact of the 'technology of materials' on biological systems, we have documented a mechanism to regulate membrane excitability, but at the same time we have also experimentally described a property of the material through the biology of neurons."
###
The work has been carried out within the Graphene Flagship supported by the European Union.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chiara Saviane - SISSA
0039-333-767-5962
Copyright © SCUOLA INTERNAZIONALE SUPERIORE DI STUDI AVANZATI
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Brain-Computer Interfaces
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








