Home > Press > Doing the nano-shimmy: New device modulates light and amplifies tiny signals
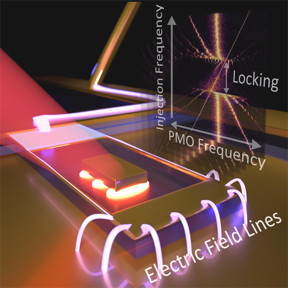 |
| This is a schematic of the first-ever plasmomechanical oscillator (PMO), developed by NIST researchers. The orange-white ovals represent the localized plasmon oscillations. The cantilever, containing the gold cuboid nanoparticle, lies dead center. The series of white curves represents the electrical field applied to the cantilever. Data at right indicates that the device can lock onto and greatly amplify weak signals that oscillate at frequencies close to those of the PMO. CREDIT B. Roxworthy/NIST |
Abstract:
Imagine a single particle, only one-tenth the diameter of a bacterium, whose miniscule jiggles induce sustained vibrations in an entire mechanical device some 50 times larger. By taking clever advantage of the interplay between light, electrons on the surface of metals, and heat, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have for the first time created a plasmomechanical oscillator (PMO), so named because it tightly couples plasmons--the collective oscillations of electrons at the surface of a metal nanoparticle--to the mechanical vibrations of the much larger device it's embedded in.
Doing the nano-shimmy: New device modulates light and amplifies tiny signals
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on April 12th, 2018The entire system, no bigger than a red blood cell, has myriad technological applications. It offers new ways to miniaturize mechanical oscillators, improve communication systems that depend on the modulation of light, dramatically amplify extremely weak mechanical and electrical signals and create exquisitely sensitive sensors for the tiny motions of nanoparticles.
NIST researchers Brian Roxworthy and Vladimir Aksyuk described their work in a recent issue of Optica.
The device consists of a gold nanoparticle, about 100 nanometers in diameter, embedded in a tiny cantilever--a miniature diving board--made of silicon nitride. An air gap lies sandwiched between these components and an underlying gold plate; the width of the gap is controlled by an electrostatic actuator--a thin gold film that sits atop the cantilever and bends toward the plate when a voltage is applied. The nanoparticle acts as a single plasmonic structure that has a natural, or resonant, frequency that varies with the size of the gap, just as tuning a guitar string changes the frequency at which the string reverberates.
When a light source, in this case laser light, shines on the system, it causes electrons in the resonator to oscillate, raising the temperature of the resonator. This sets the stage for a complex interchange between light, heat and mechanical vibrations in the PMO, endowing the system with several key properties.
By applying a small, direct-current voltage to the electrostatic actuator that squeezes the gap shut, Roxworthy and Aksyuk altered the optical frequency at which the resonator vibrates and the intensity of the laser light the system reflects. Such optomechanical coupling is highly desirable because it can modulate and control the flow of light on silicon chips and shape the propagation of light beams traveling in free space.
A second property relates to the heat generated by the resonator when it absorbs laser light. The heat causes the thin gold film actuator to expand. The expansion narrows the gap, decreasing the frequency at which the embedded resonator vibrates. Conversely, when the temperature decreases, the actuator contracts, widening the gap and increasing the frequency of the resonator.
Crucially, the force exerted by the actuator always kicks the cantilever in the same direction in which the cantilever is already traveling. If the incident laser light is powerful enough, these kicks cause the cantilever to undergo self-sustaining oscillations with amplitudes thousands of times larger than the oscillations of the device due to the vibration of its own atoms at room temperature.
"This is the first time that a single plasmonic resonator with dimensions smaller than visible light has been shown to produce such self-sustaining oscillations of a mechanical device," said Roxworthy.
The team also demonstrated for the first time that if the electrostatic actuator delivers a small mechanical force to the PMO that varies in time while the system undergoes these self-sustaining oscillations, the PMO can lock onto that tiny variable signal and greatly amplify it. The researchers showed that their device can amplify a faint signal from a neighboring system even when that signal's amplitude is as small as ten trillionths of a meter. That ability could translate into vast improvements in detecting small oscillating signals, Roxworthy says.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben P. Stein
301-975-2763
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Plasmonics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








