Home > Press > Round-the-clock power from smart bowties
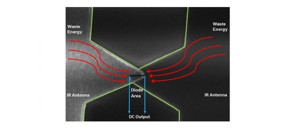 |
| Overlapping metal arms shaped like a bowtie form a 'rectenna' that captures free, renewable infrared energy. CREDIT © 2017 Atif Shamim |
Abstract:
Most sunlight striking the Earth is absorbed by its surfaces, oceans and atmosphere. As a result of this warming, infrared radiation is emitted constantly all around us--estimated to be millions of Gigawatts per second. A KAUST team has now developed a device that can tap into this energy, as well as waste heat from industrial processes, by transforming quadrillionth-of-a-second wave signals into useful electricity.
Round-the-clock power from smart bowties
Thuwal, Saudi Arabia | Posted on February 5th, 2018Unlike solar panels that are limited by daylight hours and weather conditions, infrared heat can be harvested 24 hours a day. One way to achieve this is to treat waste or infrared heat as high-frequency electromagnetic waves. Using appropriately designed antennas, collected waves are sent to a rectifier, typically a semiconductor diode, that converts alternating signals to direct current charge for batteries or power devices.
Putting these 'rectenna' designs into practice has been difficult. Because infrared emissions have very small wavelengths, they need micro- or nanoscale antennas that are not easy to fabricate or test. Additionally, infrared waves oscillate thousands of times faster than a typical semiconductor can move electrons through its junction. "There is no commercial diode in the world that can operate at such high frequency," says Atif Shamim, project leader from KAUST. "That's why we turned to quantum tunneling."
Tunneling devices, such as metal-insulator-metal (MIM) diodes, rectify infrared waves into current by moving electrons through a small barrier. Since this barrier is only a nanometer thin, MIM diodes can handle high-frequency signals on the order of femtoseconds. To generate the intense fields needed for tunneling, the team turned to a unique 'bowtie-shaped' nano-antenna that sandwiches the thin insulator film between two slightly overlapped metallic arms.
"The most challenging part was the nanoscale overlap of the two antenna arms, which required very precise alignment," says postdoctoral researcher, Gaurav Jayaswal. "Nonetheless, by combining clever tricks with the advanced tools at KAUST's nanofabrication facility we accomplished this step".
By choosing metals with different work functions, the new MIM diode could catch the infrared waves with zero applied voltage, a passive feature that switches the device on only when needed. Experiments with infrared exposure revealed the bowtie successfully harvested energy solely from the radiation, and not from thermal effects, as evidenced by a polarization-dependent output voltage.
"This is just the beginning--a proof of concept," says Shamim. "We could have millions of such devices connected to boost overall electricity generation."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
carolyn unck
Copyright © King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








