Home > Press > New Method Uses DNA, Nanoparticles and Top-Down Lithography to Make Optically Active Structures: Technique could lead to new classes of materials that can bend light, such as for those used in cloaking devices
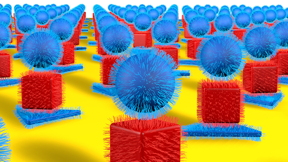 |
| Researchers have developed a new method to precisely arrange nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes in two and three dimensions, resulting in optically active superlattices. |
Abstract:
•DNA -- nature’s blueprint -- is a key tool in new method
•‘Architecture is everything when designing new materials,’ scientist says
•The structures cannot be made using any other known technique
•Powerful technique combines a workhorse fabrication method with a new one based on DNA programmability
New Method Uses DNA, Nanoparticles and Top-Down Lithography to Make Optically Active Structures: Technique could lead to new classes of materials that can bend light, such as for those used in cloaking devices
Evanston, IL | Posted on January 18th, 2018Northwestern University researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind technique for creating entirely new classes of optical materials and devices that could lead to light bending and cloaking devices -- news to make the ears of Star Trek’s Spock perk up.
Using DNA as a key tool, the interdisciplinary team took gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes and arranged them in two and three dimensions to form optically active superlattices. Structures with specific configurations could be programmed through choice of particle type and both DNA-pattern and sequence to exhibit almost any color across the visible spectrum, the scientists report.
“Architecture is everything when designing new materials, and we now have a new way to precisely control particle architectures over large areas,” said Chad A. Mirkin, the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences at Northwestern. “Chemists and physicists will be able to build an almost infinite number of new structures with all sorts of interesting properties. These structures cannot be made by any known technique.”
The technique combines an old fabrication method -- top-down lithography, the same method used to make computer chips -- with a new one -- programmable self-assembly driven by DNA. The Northwestern team is the first to combine the two to achieve individual particle control in three dimensions.
The study was published online by the journal Science today (Jan. 18). Mirkin and Vinayak P. Dravid and Koray Aydin, both professors in Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering, are co-corresponding authors.
Scientists will be able to use the powerful and flexible technique to build metamaterials -- materials not found in nature -- for a range of applications including sensors for medical and environmental uses.
The researchers used a combination of numerical simulations and optical spectroscopy techniques to identify particular nanoparticle superlattices that absorb specific wavelengths of visible light. The DNA-modified nanoparticles -- gold in this case -- are positioned on a pre-patterned template made of complementary DNA. Stacks of structures can be made by introducing a second and then a third DNA-modified particle with DNA that is complementary to the subsequent layers.
In addition to being unusual architectures, these materials are stimuli-responsive: the DNA strands that hold them together change in length when exposed to new environments, such as solutions of ethanol that vary in concentration. The change in DNA length, the researchers found, resulted in a change of color from black to red to green, providing extreme tunability of optical properties.
“Tuning the optical properties of metamaterials is a significant challenge, and our study achieves one of the highest tunability ranges achieved to date in optical metamaterials,” said Aydin, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science at McCormick.
“Our novel metamaterial platform -- enabled by precise and extreme control of gold nanoparticle shape, size and spacing -- holds significant promise for next-generation optical metamaterials and metasurfaces,” Aydin said.
The study describes a new way to organize nanoparticles in two and three dimensions. The researchers used lithography methods to drill tiny holes -- only one nanoparticle wide -- in a polymer resist, creating “landing pads” for nanoparticle components modified with strands of DNA. The landing pads are essential, Mirkin said, since they keep the structures that are grown vertical.
The nanoscopic landing pads are modified with one sequence of DNA, and the gold nanoparticles are modified with complementary DNA. By alternating nanoparticles with complementary DNA, the researchers built nanoparticle stacks with tremendous positional control and over a large area. The particles can be different sizes and shapes (spheres, cubes and disks, for example).
“This approach can be used to build periodic lattices from optically active particles, such as gold, silver and any other material that can be modified with DNA, with extraordinary nanoscale precision,” said Mirkin, director of Northwestern’s International Institute for Nanotechnology.
Mirkin also is a professor of medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and professor of chemical and biological engineering, biomedical engineering and materials science and engineering in the McCormick School.
The success of the reported DNA programmable assembly required expertise with hybrid (soft-hard) materials and exquisite nanopatterning and lithographic capabilities to achieve the requisite spatial resolution, definition and fidelity across large substrate areas. The project team turned to Dravid, a longtime collaborator of Mirkin’s who specializes in nanopatterning, advanced microscopy and characterization of soft, hard and hybrid nanostructures.
Dravid contributed his expertise and assisted in designing the nanopatterning and lithography strategy and the associated characterization of the new exotic structures. He is the Abraham Harris Professor of Materials Science and Engineering in McCormick and the founding director of the NUANCE center, which houses the advanced patterning, lithography and characterization used in the DNA-programmed structures.
The study is titled “Building Superlattices from Individual Nanoparticles via Template-Confined DNA-Mediated Assembly.” Qing-Yuan Lin, Jarad A. Mason and Zhongyang Li are first authors of the study.
The Center for Bio-Inspired Energy Science, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences (award #DE-SC0000989) and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (award numbers FA9550-12-1-0280, FA9550-14-1-0274 and FA9550-17-1-0348) supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Bob Rowley
847-491-4889
Source contacts:
Chad Mirkin
cell 847-414-4623
Koray Aydin
Vinayak Dravid
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanofabrication
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
![]() Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
Multiphoton polymerization: A promising technology for precision medicine February 28th, 2025
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








