Home > Press > Graphene based terahertz absorbers: Printable graphene inks enable ultrafast lasers in the terahertz range
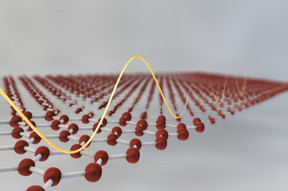 |
| Graphene Flagship researches create a terahertz saturable absorber using printable graphene inks with an order of magnitude higher absorption modulation than other devices produced to date CREDIT Graphene Flagship |
Abstract:
Graphene Flagship researches from CNR-Istituto Nanoscienze, Italy and the University of Cambridge, UK have shown that it is possible to create a terahertz saturable absorber using graphene produced by liquid phase exfoliation and deposited by transfer coating and ink jet printing. The paper, published in Nature Communications, reports a terahertz saturable absorber with an order of magnitude higher absorption modulation than other devices produced to date.
Graphene based terahertz absorbers: Printable graphene inks enable ultrafast lasers in the terahertz range
Cambridge, UK | Posted on September 13th, 2017A terahertz saturable absorber decreases its absorption of light in the terahertz range (far infrared) with increasing light intensity and has great potential for the development of terahertz lasers, with applications in spectroscopy and imaging. These high-modulation, mode-locked lasers open up many prospects in applications where short time scale excitation of specific transitions are important, such as time-resolved spectroscopy of gasses and molecules, quantum information or ultra-high speed communication.
"We started working on saturable terahertz absorbers to solve the problem of producing a miniaturized mode-locked terahertz laser with thin and flexible integrated components that also had good modulation" said Graphene Flagship researcher Miriam Vitiello from CNR-Istituto Nanoscienze in Italy.
Graphene is a promising saturable absorber as it has intrinsic broadband operations and ultrafast recovery time along with an ease of fabrication and integration, as first demonstrated in ultra-fast infra-red lasers by Flagship partner University of Cambridge. In the terahertz range, the present paper exploits graphene produced by liquid phase exfoliation, a method ideally suited to mass production, to prepare inks, easily deposited by transfer coating or ink jet printing
"It was important to us to use a type of graphene that could be integrated into the laser system with flexibility and control" said Vitiello "Ink jet printing along with transfer coating achieved that."
Using mode-locked lasers to produce ultra fast pulses in the terahertz range can have interesting and exciting uses. "These devices could have applications in medical diagnostics when time of flight topography is of importance - you could see a tumour inside a tissue" said Vitiello.
Frank Koppens, of the Institute of Photonic Sciences in Spain, is the leader of the Graphene Flagship's Photonics and Optoelectronics Work Package, which focuses on developing graphene-based technologies for imaging and sensing, data transfer and other photonics applications. "This is a new discovery with immediate impact on applications. Clearly, this is a case where graphene beats existing materials in terms of efficiency, scalability, compactness and speed" he said.
Andrea C. Ferrari, Science and Technology Officer of the Graphene Flagship, and Chair of its Management Panel added "It is an important milestone to have demonstrated that easily produced and printable graphene inks can also serve to enable ultrafast lasers in the terahertz range. Since the Flagship's inception, a variety of lasers have been made covering the visible to IR spectral range, but now the important THz range, with applications in security and medical diagnostic, is finally made accessible by graphene, starting yet another possible application field."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sian Fogden
44-012-237-62418
Copyright © Graphene Flagship
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








