Home > Press > Coupling a nano-trumpet with a quantum dot enables precise position determination
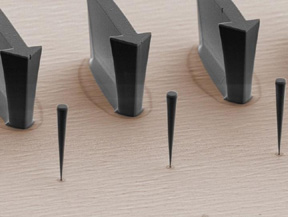 |
| Trumpet-shaped nanowires with a length of about 10 micrometers are coupled to quantum dots located at their bases. The movement of the nanowire can be detected with a sensitivity of 100 femtometers by changing the wavelength of the light emitted by the quantum dots. The arrows are important for fabrication and help to locate the nanowires. CREDIT Grenoble Alps University |
Abstract:
Scientists from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the University of Basel have succeeded in coupling an extremely small quantum dot with 1,000 times larger trumpet-shaped nanowire. The movement of the nanowire can be detected with a sensitivity of 100 femtometers via the wavelength of the light emitted by the quantum dot. Conversely, the oscillation of the nanowire can be influenced by excitation of the quantum dot with a laser. Nature Communications published the results.
Coupling a nano-trumpet with a quantum dot enables precise position determination
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on July 14th, 2017Professor Richard Warburton and Argovia Professor Martino Poggio's teams in the Department of Physics and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel worked with colleagues from Grenoble Alps University and the Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) in Grenoble to couple a microscopic mechanical resonator with a nano-scale quantum dot. They used nanowires made of gallium arsenide that are about 10 micrometers long and have a diameter of a few micrometers at the top. The wires taper sharply downwards and therefore look like tiny trumpets arranged on the substrate. Near the base, which is only about 200 nanometers wide, the scientists placed a single quantum dot that can emit individual light particles (photons).
Excitations lead to strains
If the nanowire oscillates back and forth due to thermal or electrical excitation, the relatively large mass at the wide end of the nano-trumpet produces large strains in the wire that affect the quantum dot at the base. The quantum dots are squeezed together and pulled apart; as a result, the wavelength and thus the color of the photons emitted by the quantum dot change. Although the changes are not particularly large, sensitive microscopes with very stable lasers - specifically developed in Basel for such measurements - are capable of precise detection of the wavelength changes. The researchers can use the shifted wavelengths to detect the motion of the wire with a sensitivity of only 100 femtometers. They expect that by exciting the quantum dot with a laser, the oscillation of the nanowire can be increased or decreased as desired.
Potential uses in sensor and information technology
"We are particularly fascinated by the fact that a link between objects of such different sizes is possible," says Warburton. There are also various potential applications for this mutual coupling. "For example, we can use these coupled nanowires as sensitive sensors to analyze electrical or magnetic fields," explains Poggio, who is investigating the possible applications with his team. "It may also be possible to place several quantum dots on the nanowire, to use the motion to link them together and so pass on quantum information," adds Warburton, whose group focuses on the diverse use of quantum dots in photonics.
Artificial atoms with special properties
Quantum dots are nanocrystals, and are also known as artificial atoms because they behave similarly to atoms. With a typical extent of 10 to 100 nanometers, they are significantly larger than actual atoms. Their size and shape, as well as the number of electrons, can vary. The electrons' freedom of movement in the quantum dots is significantly restricted; the resulting quantum effects give them very special optical, magnetic and electrical properties. For example, quantum dots are able to emit individual light particles (photons) after excitation, which can then be detected using a tailor-made laser microscope.
###
Original source
Mathieu Munsch, Andreas V. Kuhlmann, Davide Cadeddu, Jean-Michel
Gérard, Julien Claudon, Martino Poggio, and Richard J. Warburton
Resonant driving of a single photon emitter embedded in a mechanical oscillator
Nature Communications (2017) | DOI: s41467-017-00097-3
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olivia Poisson
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








