Home > Press > ANU invention may help to protect astronauts from radiation in space
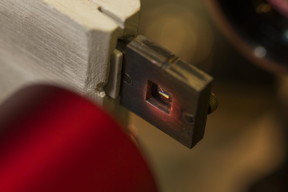 |
| The sample here contains hundreds of thousands of nanoparticles that manipulate the incoming light. CREDIT Stuart Hay, ANU |
Abstract:
Scientists at The Australian National University (ANU) have designed a new nano material that can reflect or transmit light on demand with temperature control, opening the door to technology that protects astronauts in space from harmful radiation.
ANU invention may help to protect astronauts from radiation in space
Canberra, Australia | Posted on July 3rd, 2017Lead researcher Dr Mohsen Rahmani from ANU said the material was so thin that hundreds of layers could fit on the tip of a needle and could be applied to any surface, including spacesuits.
"Our invention has a lot of potential applications, such as protecting astronauts or satellites with an ultra-thin film that can be adjusted to reflect various dangerous ultraviolet or infrared radiation in different environments," said Dr Rahmani, an Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery Early Career Research Fellow at the Nonlinear Physics Centre within the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
"Our technology significantly increases the resistance threshold against harmful radiation compared to today's technologies, which rely on absorbing radiation with thick filters."
Co-researcher Associate Professor Andrey Miroshnichenko said the invention could be tailored for other light spectrums including visible light, which opened up a whole array of innovations, including architectural and energy saving applications.
"For instance, you could have a window that can turn into a mirror in a bathroom on demand, or control the amount of light passing through your house windows in different seasons," said Dr Miroshnichenko from the Nonlinear Physics Centre within the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
"What I love about this invention is that the design involved different research disciplines including physics, materials science and engineering."
Co-lead researcher Dr Lei Xu said achieving cost-efficient and confined temperature control such as local heating was feasible.
"Much like your car has a series of parallel resistive wires on the back windscreen to defog the rear view, a similar arrangement could be used with our invention to confine the temperature control to a precise location," said Dr Xu from the Nonlinear Physics Centre within the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering.
The innovation builds on more than 15 years of research supported by the ARC through CUDOS, a Centre of Excellence, and the Australian National Fabrication Facility.
The research is published in Advanced Functional Materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
FOR INTERVIEW:
Dr Mohsen Rahmani
ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering
M: +61 435 086 036
E:
Associate Professor Andrey Miroshnichenko
ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering
T: +61 2 6125 3964
E:
Dr Lei Xu
ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering
T: +61 2 6125 9203
E:
FOR MEDIA ASSISTANCE:
Will Wright
ANU media team
T: +61 2 6125 7979
M: +61 478 337 740
E:
Copyright © Australian National University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
Understanding the mechanism of non-uniform formation of diamond film on tools: Paving the way to a dry process with less environmental impact March 24th, 2023
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








