Home > Press > Enhanced photocatalytic activity by Cu2O nanoparticles integrated H2Ti3O7 nanotubes
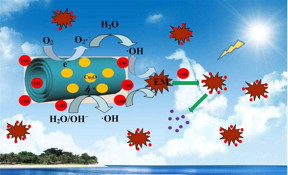 |
| The suggested mechanism of photocatalytic oxidization of EM over Cu2O@H2Ti3O7 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation. Under the sunlight irradiation, photo-generated electrons (e?) of nanocomposite aggregated on nanotubes, and holes (h?) aggregated on Cu2O nanoparticles, which will reduce the bandgap energy and prolong the effective separation of photo-induced electron-hole pairs, enhance eventually the photocatalytic activity. It causes a large number of the hydroxy radical groups (·OH) generated on nanocomposite, which will effectively oxidize EM due to the synergistic effect between them to form heterojunction structure. Therefore, nanocomposite exhibits the excellent photocatalytic performance. CREDIT NANO Journal |
Abstract:
Why do we construct nanocomposite for the photocatalytic oxidation desulfurization?
Current hydrodesulfurization (HDS) technology is hard to remove thiols and refractory thiophenic compounds to a minimum in fuels. Moreover, the HDS technology requires severe operation conditions, along with other disadvantages in deep desulfurization. Therefore, considerable attention has been paid to non-HDS techniques, such as adsorption, biodesulfurization and photocatalytic oxidation, etc. Among them, the photocatalytic oxidation desulfurization is the most ideal "green chemistry" technology for deep desulfurization with mild operating conditions. Some researchers have reported nanocomposite as an effective photocatalytic functional material than the host alone, such as nanotube arrays, etc.
Enhanced photocatalytic activity by Cu2O nanoparticles integrated H2Ti3O7 nanotubes
Singapore | Posted on June 21st, 2017Titanate nanotubes attracted a wide attention for the high photocatalytic activity under UV light irradiation. However, titanates have a relatively wide band gap and is utilize only under UV light, thus the photocatalytic activity is limitation. Moreover, when Cu2O is used as a photocatalyst alone, it is a limitation what the electrons and holes excited by light cannot be transferred efficiently and are easy to recombine. Some team of researchers introduced an innovative strategy by compositing Cu2O nanoparticles with titanate nanotubes, which will result in the stronger visible spectral response and wider absorbance. This technology provides a new approach to reduce the bandgap energy and prolong the separation of photo-generated electron-hole pairs, which resulted in better photocatalytic activities for photodegradation of organic pollutants more thoroughly.
The most significant aspect of my study: Composting Cu2O nanoparticles with H2Ti3O7 nanotubes as an effective photocatalyst applied in desulfurization, it was rarely reported that the construction and desulfurization application of this functional materials before we research. At first, the photocatalytic oxidation desulfurization is the most ideal "green chemistry" technology for deep desulfurization with mild operating conditions than the current HDS technology. Next, We have synthesized the trititanate nanotubes. Previous researches demonstrated that some layered titanates were better photocatalysts, and the corresponding nanosheets and nanotubes even showed much higher photocatalytic activities than the original layered compound. In addition, we have constructed the nanocomposite, the mesoporous nanoscroll composites possess obviously higher photocatalytic activities than guest oxide nanoparticles or host layered materials alone. The researches suggest that layered materials doped with guest nanoparticles can not only reduce the bandgap, but also inhibit the recombination of photoinduced electron-hole pairs. Therefore, we employ Cu2O nanoparticles integrated H2T3O7 nanotubes by a facile hydrothermal method, it shows that nanocomposite exhibits the excellent photocatalytic performance due to the stronger visible spectral response and wider absorbance, this research that could help develop new energy resources (solar energy) and oxidize organic pollutants for protection of the environment.
###
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21271008, 21071004).
Addition co-authors of the paper are Lei Xu, Jie He, Lifang Hu, Bin Wang and Liangguo Da, they all come from Anhui University of Science and Technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Lim
646-65775 x247
Corresponding author for this study is Jie He,
Copyright © World Scientific
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








