Home > Press > Zap! Graphene is bad news for bacteria: Rice, Ben-Gurion universities show laser-induced graphene kills bacteria, resists biofouling
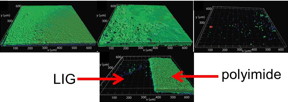 |
| In the top row, the growth of biofilm on surfaces with a solution containing Pseudomonas aeruginosa is observed on, from left, polyimide, graphite and laser-induced graphene surfaces. Green, red and blue represent live bacteria, dead bacteria and extracellular polymeric substances, respectively. At bottom, a sheet of polyimide burned on the left to leave laser-induced graphene shows the graphene surface nearly free of growth. (Credit: Arnusch Lab/Ben-Gurion University of the Negev) |
Abstract:
Scientists at Rice University and Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have discovered that laser-induced graphene (LIG) is a highly effective anti-fouling material and, when electrified, bacteria zapper.
In this real-time video, Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria tagged with green fluorescent protein, which appear as bright dots, are drawn to an anode of laser-induced graphene, where they die. The anode at the top, which is separated from a cathode by a 100-micron channel, carries a small voltage that boosts its antibacterial properties. (Credit: Arnusch Lab/Ben-Gurion University of the Negev)
Zap! Graphene is bad news for bacteria: Rice, Ben-Gurion universities show laser-induced graphene kills bacteria, resists biofouling
Houston, TX | Posted on May 22nd, 2017LIG is a spongy version of graphene, the single-atom layer of carbon atoms. The Rice lab of chemist James Tour developed it three years ago by burning partway through an inexpensive polyimide sheet with a laser, which turned the surface into a lattice of interconnected graphene sheets. The researchers have since suggested uses for the material in wearable electronics and fuel cells and for superhydrophobic or superhydrophilic surfaces.
According to their report in the American Chemical Society's ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, LIG also protects surfaces from biofouling, the buildup of microorganisms, plants or other biological material on wet surfaces.
"This form of graphene is extremely resistant to biofilm formation, which has promise for places like water-treatment plants, oil-drilling operations, hospitals and ocean applications like underwater pipes that are sensitive to fouling," Tour said. "The antibacterial qualities when electricity is applied is a great additional benefit."
When used as electrodes with a small applied voltage, LIG becomes the bacterial equivalent of a backyard bug zapper. Tests without the charge confirmed what has long been known -- that graphene-based nanoparticles have antibacterial properties. When 1.1 to 2.5 volts were applied, the highly conductive LIG electrodes "greatly enhanced" those properties.
Under the microscope, the researchers watched as fluorescently tagged Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria in a solution with LIG electrodes above 1.1 volts were drawn toward the anode. Above 1.5 volts, the cells began to disappear and vanished completely within 30 seconds. At 2.5 volts, bacteria disappeared almost completely from the surface after one second.
The Rice lab partnered with Professor Christopher Arnusch, a lecturer at the BGU Zuckerberg Institute for Water Research who specializes in water purification. Arnusch's lab tested LIG electrodes in a bacteria-laden solution with 10 percent secondary treated wastewater and found that after nine hours at 2.5 volts, 99.9 percent of the bacteria were killed and the electrodes strongly resisted biofilm formation.
The researchers suspect bacteria may meet their demise through a combination of contact with the rough surface of LIG, the electrical charge and toxicity from localized production of hydrogen peroxide. The contact may be something like a knee hitting pavement, but in this case, the bacteria are all knee and the sharp graphene edges quickly destroy their membranes.
Fortunately, LIG's anti-fouling properties keep dead bacteria from accumulating on the surface, Tour said.
"The combination of passive biofouling inhibition and active voltage-induced microbial removal will likely make this a highly sought-after material for inhibiting the growth of troublesome natural fouling that plagues many industries," Tour said.
Swatantra Singh, a postdoctoral fellow at BGU, and Yilun Li, a graduate student at Rice, are lead authors of the paper. Co-authors are Avraham Be'er, a senior lecturer, and Yoram Oren, an emeritus professor, both of BGU. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The research was supported by the United States−Israel Binational Science Foundation, the Canadian Associates of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Quebec Region, the Israel Science Foundation, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
AT BGU:
Andrew Lavin
516-944-4486
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








