Home > Press > Three-dimensional Direction-dependent Force Measurement at the Subatomic Scale: International researchers led by Osaka University develop a microscopy technique to probe materials at the subatomic scale in multiple directions simultaneously
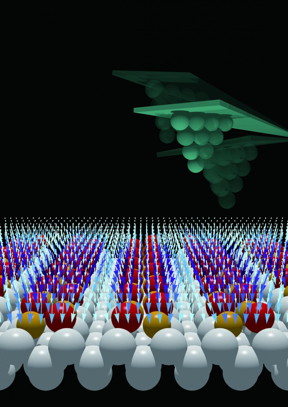 |
| Bimodal atomic force microscopy provides three-dimensional force vector maps with subatomic resolution. The cantilever is simultaneously oscillated laterally and vertically to determine the vector mapping over the buckled dimers on the Ge(001) surface. CREDIT Osaka University |
Abstract:
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is an extremely sensitive technique that allows us to image materials and/or characterize their physical properties on the atomic scale by sensing the force above material surfaces using a precisely controlled tip. However, conventional AFM only provides the surface normal component of the force (the Z direction) and ignores the components parallel to the surface (the X and Y directions). To fully characterize materials used in nanoscale devices, it is necessary to obtain information about parameters with directionality, such as electronic, magnetic, and elastic properties, in more than just the Z direction. That is, it is desirable to measure these parameters in the X and Y directions parallel to the surface of a material as well. Measuring the distribution of such material parameters on the atomic scale will increase our understanding of chemical composition and reactions, surface morphology, molecular manipulation, and nanomachine operation.
Three-dimensional Direction-dependent Force Measurement at the Subatomic Scale: International researchers led by Osaka University develop a microscopy technique to probe materials at the subatomic scale in multiple directions simultaneously
Osaka, Japan | Posted on May 11th, 2017A research group at Osaka University has recently developed an AFM-based approach called "bimodal AFM" to obtain information about material surfaces in the X, Y, and Z directions (that is, in three dimensions) on the subatomic scale. The researchers measured the total force between an AFM tip and material surface in the X, Y, and Z directions using a germanium (Ge) surface as a substrate. Their collaborative partner, the Institute of Physics of the Slovak Academy of Sciences, contributed computer simulations of the tip-surface interactions. The bimodal AFM approach was recently reported in Nature Physics.
"A clean Ge(001) surface has alternately aligned anisotropic dimers, which are rotated by 90° across the step, meaning they show a two-domain structure," explains first author Yoshitaka Naitoh. "We probed the force fields from each domain in the vertical direction by oscillating the AFM tip at the flexural resonance frequency and in the parallel direction by oscillating it at the torsional one."
The team first expressed the force components as vectors, providing the vector distribution above the surface at the subatomic scale. The computer simulation supported the experimental results and shed light on the nature of chemical tip termination and morphology and, in particular, helped to clarify the outstanding questions regarding the tip-surface distances in the experiment.
"We measured the magnitude and direction of the force between the AFM tip and Ge surface on a subatomic scale in three dimensions," says Naitoh. "Such measurements will aid understanding of the structure and chemical reactions of functionalized surfaces."
The developed bimodal AFM approach will allow researchers to investigate the physical properties of materials in greater detail on the nanoscale, which should facilitate development of devices, nanotechnology, and friction/lubrication systems.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Saori Obayashi
81-661-055-886
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Friction/ Tribology
![]() Perking up and crimping the 'bristles' of polyelectrolyte brushes December 13th, 2017
Perking up and crimping the 'bristles' of polyelectrolyte brushes December 13th, 2017
![]() Movable microplatform floats on a sea of droplets: New technique offers precise, durable control over tiny mirrors or stages December 19th, 2016
Movable microplatform floats on a sea of droplets: New technique offers precise, durable control over tiny mirrors or stages December 19th, 2016
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








