Home > Press > The Catholic University of Rome uses the JPK NanoWizard® AFM & CellHesion® systems to understand how cells sense and respond to mechanical stimuli
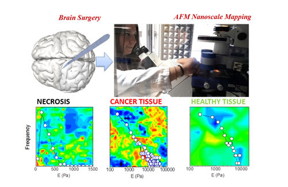 |
| Examples of cell tissue modulus vs frequency maps obtained using the JPK NanoWizard® and CellHesion® systems |
Abstract:
JPK Instruments, a world-leading manufacturer of nanoanalytic instrumentation for research in life sciences and soft matter, reports on the work of Professor Marco De Spirito's research group at the Catholic University of Rome. The group uses a NanoWizard® AFM and CellHesion® module to study how cells sense and respond to mechanical stimuli.
The Catholic University of Rome uses the JPK NanoWizard® AFM & CellHesion® systems to understand how cells sense and respond to mechanical stimuli
Berlin, Germany | Posted on April 5th, 2017Dr Gabriele Ciasca and Professor Massimiliano Papi are members of the research team of Professor Marco De Spirito in the Institute of Physics at the Catholic University of Rome, Italy. One of the main goals of their group is the investigation of how cells sense and respond to physical and mechanical stimuli. Professor De Spirito says that a deeper knowledge of cell biomechanics can boost the understanding of how mechanical properties affect and are affected by the development of many pathological states including cancer.
An example of this research has been reported in a recent clinical paper published in the high impact factor journal Nanoscale. This paper, “Nano-mechanical signature of brain tumours,” was carried out in collaboration with Dr Tanya Enny Sassun during her PhD in the group of Professor Delfini, head of the Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Neurosurgery (Sapienza University of Rome). The research group studied the biomechanical fingerprint of the two most frequent malignant and benign brain tumours: the highly aggressive Glioblastoma and the slowly-growing Meningioma. They investigated the complex biophysical interplay between neoplastic cells and the tumour microenvironment using the NanoWizard® AFM from JPK. This showed that AFM is able to easily distinguish between cancerous and healthy peritumoural tissues.
Eleonora Minelli - who works as a PhD student in the group of Professor De Spirito - takes up the story of how this work has been extended. “The acquisition of elasticity maps of surgically removed tissues is plagued by the problem of roughness that is often larger than the available range of the piezoelectric actuator. This meant we have had to develop a novel procedure that allowed us to acquire elasticity maps of an unparalleled size (up to 100 µm x 100 µm). We achieved this result thanks to the use of the JPK CellHesion® module that can be easily integrated to our NanoWizard®. This has a z-piezoelectric actuator with a range of 100 µm. These results open up many applications in nanomedicine and have the potential to boost the use of AFM in clinical practice. AFM, together with confocal microscopy and electron microscopy, are key tools in this research area because it allows us to probe mechanical and topographical properties of molecules, cells and tissues in nearly all environments.”
Dr Ciasca, Professor Papi and their colleagues have a lot of experience using different makes of AFM. “The members of our group have been working with many general-purpose AFM set-ups. Now, we are deeply convinced that the JPK NanoWizard® offers one of the best suited experimental set-ups for the investigation of biological systems. There are a number of reasons for this. The instrument has an easy, accurate and effective cantilever calibration procedure. We believe this is a key advantage of this platform as it ensures reproducibility and reliability of results. This is particularly important when dealing with the nanoscale mechanical properties of cells and tissues that are intrinsically subjected to a large biological variability. The geometry of the scanning head is a unique characteristic of the JPK NanoWizard®. It opens the possibility to investigate cells and tissues directly within conventional petri dishes in a liquid environment. This key characteristic allowed us to investigate the mechanical and structural properties of living cells in their own environment without the need of fixation procedures that deeply alter mechanical and morphological properties. Most importantly, the NanoWizard® in our laboratory offers effective integration with a conventional inverted fluorescence microscopy which allows us to combine fluorescence and optical images with elasticity maps.”
The Group publishes extensively. Some of their most recent key publications include:
Nano-mechanical signature of brain tumours (Nanoscale 8 (47), 19629-19643) by G Ciasca et al.
Mapping viscoelastic properties of healthy and pathological red blood cells at the nanoscale level (Nanoscale, 2015,7, 17030-17037 DOI: 10.1039/C5NR03145A) by G Ciasca et al.
Bacteria Meet Graphene: Modulation of Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Interaction with Human Pathogens for Effective Antimicrobial Therapy (ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2017) by V Palmieri et al.
Mechanical and structural comparison between primary tumor and lymph node metastasis cells in colorectal cancer (Soft Matter, 2015,11, 5719-5726 DOI: 10.1039/C5SM01089F) by Dr V Palmieri et al.
For more details about JPK's AFM systems and their applications for the materials, life & nano sciences, please contact JPK on +49 30726243 500. Alternatively, please visit the web site: www.jpk.com/ or see more on Facebook: www.jpk.com/facebook and on You Tube: www.youtube.com/jpkinstruments.
####
About JPK Instruments
JPK Instruments AG is a world-leading manufacturer of nanoanalytic instruments - particularly atomic force microscope (AFM) systems and optical tweezers - for a broad range of applications reaching from soft matter physics to nano-optics, from surface chemistry to cell and molecular biology. From its earliest days applying atomic force microscope (AFM) technology, JPK has recognized the opportunities provided by nanotechnology for transforming life sciences and soft matter research. This focus has driven JPK's success in uniting the worlds of nanotechnology tools and life science applications by offering cutting-edge technology and unique applications expertise. Headquartered in Berlin and with direct operations in Dresden, Cambridge (UK), Singapore, Tokyo, Shanghai (China), Paris (France) and Carpinteria (USA), JPK maintains a global network of distributors and support centers and provides on the spot applications and service support to an ever-growing community of researchers.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
JPK Instruments AG
Colditzstrasse 34-36
Haus 13, Eingang B
Berlin 12099
Germany
T +49 30726243 500
F +49 30726243 999
http://www.jpk.com/
Talking Science Limited
39 de Bohun Court
Saffron Walden
Essex CB10 2BA UK
T +44(0)1799 521881
M +44(0)7843 012997
www.talking-science.com.
Copyright © JPK Instruments
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








