Home > Press > Bio-inspired energy storage: A new light for solar power: Graphene-based electrode prototype, inspired by fern leaves, could be the answer to solar energy storage challenge
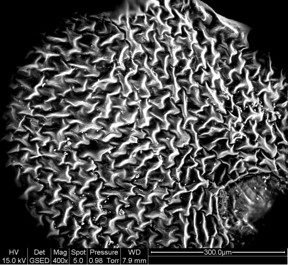 |
| This is a western swordfern leaf magnified 400 times, showing the self-repeating fractal pattern of its veins. CREDIT RMIT University |
Abstract:
Inspired by an American fern, researchers have developed a groundbreaking prototype that could be the answer to the storage challenge still holding solar back as a total energy solution.
Bio-inspired energy storage: A new light for solar power: Graphene-based electrode prototype, inspired by fern leaves, could be the answer to solar energy storage challenge
Melbourne, Australia | Posted on April 2nd, 2017The new type of electrode created by researchers from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, could boost the capacity of existing integrable storage technologies by 3000 per cent.
But the graphene-based prototype also opens a new path to the development of flexible thin film all-in-one solar capture and storage, bringing us one step closer to self-powering smart phones, laptops, cars and buildings.
The new electrode is designed to work with supercapacitors, which can charge and discharge power much faster than conventional batteries. Supercapacitors have been combined with solar, but their wider use as a storage solution is restricted because of their limited capacity.
RMIT's Professor Min Gu said the new design drew on nature's own genius solution to the challenge of filling a space in the most efficient way possible -- through intricate self-repeating patterns known as "fractals".
"The leaves of the western swordfern are densely crammed with veins, making them extremely efficient for storing energy and transporting water around the plant," said Gu, Leader of the Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence Nanophotonics and Associate Deputy Vice-Chancellor for Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship at RMIT.
"Our electrode is based on these fractal shapes -- which are self-replicating, like the mini structures within snowflakes -- and we've used this naturally-efficient design to improve solar energy storage at a nano level.
"The immediate application is combining this electrode with supercapacitors, as our experiments have shown our prototype can radically increase their storage capacity -- 30 times more than current capacity limits.
"Capacity-boosted supercapacitors would offer both long-term reliability and quick-burst energy release - for when someone wants to use solar energy on a cloudy day for example -- making them ideal alternatives for solar power storage."
Combined with supercapacitors, the fractal-enabled laser-reduced graphene electrodes can hold the stored charge for longer, with minimal leakage. The fractal design reflected the self-repeating shape of the veins of the western swordfern, Polystichum munitum, native to western North America.
Lead author, PhD researcher Litty Thekkekara, said because the prototype was based on flexible thin film technology, its potential applications were countless.
"The most exciting possibility is using this electrode with a solar cell, to provide a total on-chip energy harvesting and storage solution," Thekkekara said.
"We can do that now with existing solar cells but these are bulky and rigid. The real future lies in integrating the prototype with flexible thin film solar - technology that is still in its infancy.
"Flexible thin film solar could be used almost anywhere you can imagine, from building windows to car panels, smart phones to smart watches. We would no longer need batteries to charge our phones or charging stations for our hybrid cars.
"With this flexible electrode prototype we've solved the storage part of the challenge, as well as shown how they can work with solar cells without affecting performance. Now the focus needs to be on flexible solar energy, so we can work towards achieving our vision of fully solar-reliant, self-powering electronics."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Min Gu
61-399-252-128
Copyright © RMIT University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The research is published in Scientific Reports on Friday 31 March:
The research is published in Scientific Reports on Friday 31 March:
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








